回溯与剪枝
当递归所衍生出的子节点不符合条件时,就该“看到不对劲就撤退”——中途停止并返回。这个思路就是回溯。在回溯中用于减少子节点的拓展函数就是剪枝函数。
其难度主要在于拓展子节点的时候如何构造停止递归并返回的条件。
以HDU 2553 N皇后为例
题目
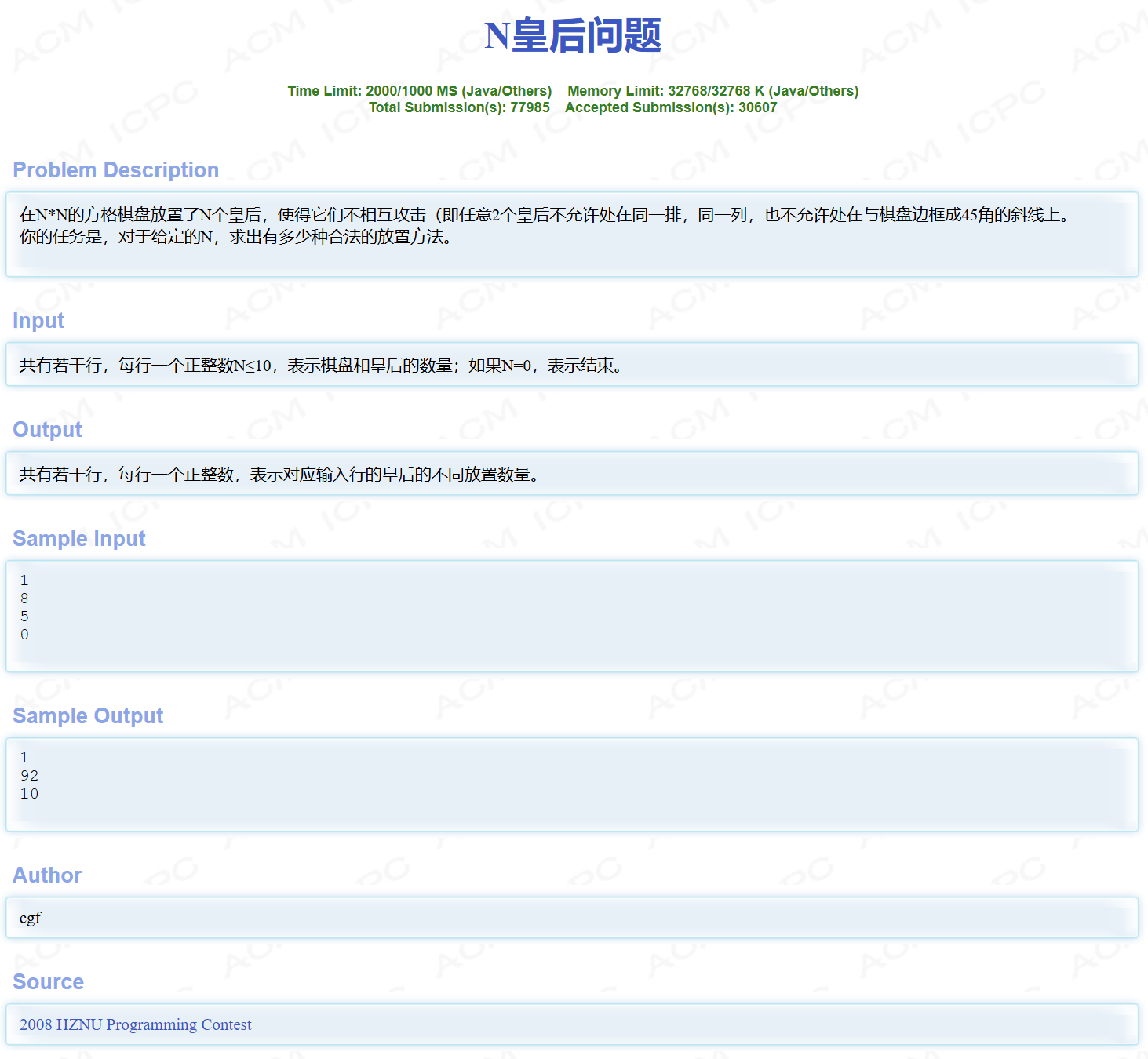
不同行: old_x=new_x
不同列: old_y=new_y
不同对角线: abs(old_x−new_x)=abs(old_y−new_y)
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,lie[11],ans[11],sum;
bool check(int newx,int newy){
for(int i=0;i<newx;i++){
if(lie[i]==newy || abs(i-newx)==abs(lie[i]-newy))
return false;
}
return true;
}
void dfs(int newx){
if(newx==n){
sum++;
return;
}
for(int newy=0;newy<n;newy++){
if(check(newx,newy)){
lie[newx]=newy;
dfs(newx+1);
}
}
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
for(n=0;n<=10;n++){
memset(lie,0,11);
sum=0;
dfs(0);
ans[n]=sum;
}
while(cin >> n){
if(n==0) return 0;
cout << ans[n] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
A*
A* 相当于是 BFS+贪心 ,是最短路里比较简单的一种算法。A*通常与曼哈顿距离扯上联系。
曼哈顿距离:两个点在标准坐标系上的实际距离,也称为出租车距离。
A*算法的一般性描述:在搜索过程中,用一个评估函数对当前情况进行评估,得到最好的状态,从这个状态继续搜索,直到目标。
以下是用A*算法来实现的八数码。manhadun()是评估函数,来评估某个状态里的每个数距离它的最终位置的距离之和,并把这个距离之和和这个状态对应的步数存进优先队列(小根堆)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string goal="123804765",start;
int explore[][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0},nextx,nexty,
goer[][2]={0,0,0,0,0,1,0,2,1,2,2,2,2,1,2,0,1,0};
#define check (nextx>=0 && nextx<3 && nexty>=0 && nexty<3)
int manhadun(string s){
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<9;i++){
int t = s[i]-'0';
if(t) sum += abs(i/3-goer[t][0])+abs(i%3-goer[t][1]);
}
return sum;
}
int astar(string s){
unordered_map <string,int> um;
priority_queue <pair<int,string>> q;
q.push({-manhadun(s),s});um[s]=0;
while(!q.empty()){
auto a=q.top();q.pop();
string st = a.second;
if(st==goal) return um[st];
int Index = st.find('0');
int x=Index/3,y=Index%3;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
nextx=x+explore[i][0];nexty=y+explore[i][1];
if(check){
string t=st;
swap(t[Index],t[nextx*3+nexty]);
if(!um.count(t)){
um[t]=um[st]+1;
q.push({-(um[t]+manhadun(t)),t});
}
}
}
}
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> start;
cout << astar(start) << '\n';
return 0;
}
|
迭代加深搜索 IDDFS
当搜索树深度极深,宽度极广,DFS陷入递归无法返回、BFS队列空间直接爆炸,此时就可以采取迭代加深搜索 IDDFS
IDDFS结合了DFS和BFS。迭代过程上,在每一层的广度上采用了BFS,在具体实现上是DFS,大概的操作是:
-
先设定搜索深度为1,用DFS搜索到第1层即停止。也就是说,用DFS搜索一个深度为1的搜索树。
-
如果没有找到答案,再设定深度为2,用 DFS 搜索前两层即停止。也就是说,用DFS搜索一个深度为2的搜索树。
-
继续设定深度为3、4……逐步扩大 DFS的搜索深度,直到找到答案。
以 埃及分数 为例
题目

该题的搜索树深度和宽度都可能是无穷的,所以要用IDDFS
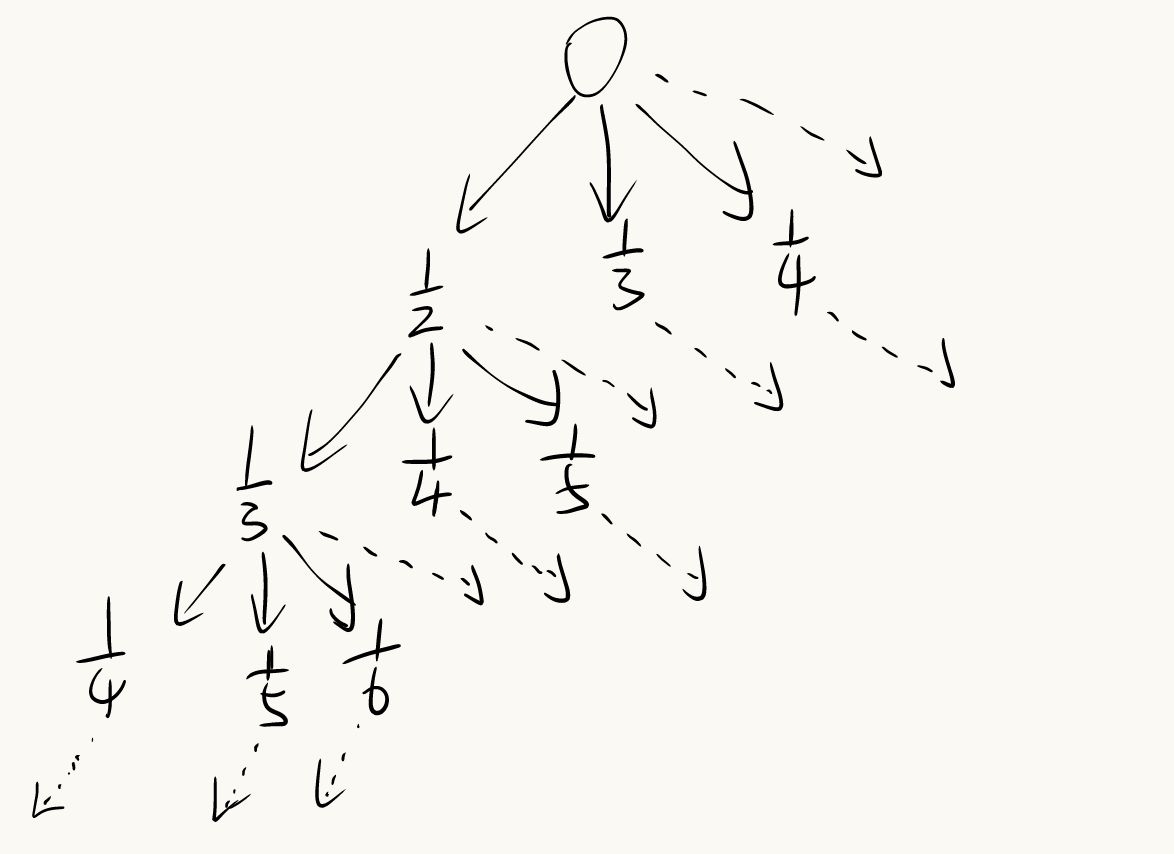
这一层找到了就不会去下一层找了,所以ans和temp的分母数量是相同的,也就是该层的层数
每一层搜索分母的起始值为i=b/a+1,i是分母,+1是因为找的分数要比题目给的分数小
每一层搜索分母的时候也有个限度,不可能无限搜吧,这个限度就是:
如果 剩余分母个数/分母 < 题目给的分数 ,即(deep-d+1)/i < a/b,那么这层就不用搜了,因为这层剩下的分数之和的最大值就是(deep-d+1)/i,如果这小于a/b了,那么这层分数再怎么累加也比a/b小。可以放缩证明,证明如下:

代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e7;
int ans[maxn+2],temp[maxn+2],pd=0,deep;
int gcd(int a,int b){
return (b==0 ? a:gcd(b,a%b));
}
void simp(int &a,int &b){
int gys=gcd(a,b);
a=a/gys;
b=b/gys;
}
void iddfs(int a,int b,int d){
if(d==deep){
if(b%a) return;
if(temp[deep-1]==b/a) return;
pd=1;
temp[d]=b/a;
int pd1=0;
if(ans[d]>temp[d]) memcpy(ans,temp,sizeof(int)*(d+1));
return;
}
for(int i=max(temp[d-1]+1,b/a+1);;i++){
if(b*(deep-d+1)<a*i) break;
temp[d]=i;
int a_1=a*i-b,b_1=b*i;
simp(a_1,b_1);
iddfs(a_1,b_1,d+1);
}
}
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
simp(a,b);
if(!b%a) cout << b/a << '\n';
else{
for(deep=2;;deep++){
ans[1]=0,ans[deep]=maxn;
iddfs(a,b,1);
if(pd) break;
}
for(int i=1;i<=deep;i++) cout << ans[i] << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
Dijkstra
迪杰斯特拉简单概括为 BFS+贪心,是一种单源最短路算法,一次计算能得到从一个起点到其它所有点的最短距离长度、最短路径的途径点。注意,dijkstra不能做边权为负数的题目。
Dijkstra的核心思想是:每次从未访问过的点中,选择距离起点最近的点作为新的起点。
Dijkstra的复杂度:设图有 n 个点, m 条边。稀疏图复杂度为 O((m+n)log2n) ,但是在稠密图的情况下复杂度会上升到 O(n2log2n) 。
来看看具体做法吧:
- 从起点 s 出发,用BFS扩展它的邻居节点,把这些邻居节点放到一个集合 A 中,并记录这些点到起点 s 的距离。
- (1) 在集合 A 中选择距离起点最近的点 v,作为新的起点,然后用BFS扩展它的邻居节点,把这些邻居节点放到集合 A 中
(2) 如果 v 的邻居经过 v 的中转,到 s 的距离更短,就更新这些邻居到 s 的距离
(3) 从集合 A 中移除 v ,后续不再处理它
- 重复第2步,直到集合 A 为空。
模板题:

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const long long INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
const int N = 3e5+2;
struct edge{
int from, to;
long long w;
edge(int a,int b,long long c) : from(a),to(b),w(c) {}
};
vector <edge> e[N];
struct node{
int id; long long n_dis;
node(int b,long long c){id = b;n_dis = c;}
bool operator < (const node & a) const
{return n_dis > a.n_dis;}
};
int n,m;
int pre[N];
void print_path(int s,int t){
if(s == t) {cout << s << '\n';return;}
print_path(s,pre[t]);
cout << t << '\n';
}
long long dis[N];
bool done[N];
void dijkstra(){
int s = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){dis[i] = INF;done[i] = false;}
dis[s] = 0;
priority_queue <node> q;
q.push({s,dis[s]});
while(!q.empty()){
node u = q.top();
q.pop();
if(done[u.id]) continue;
done[u.id] = true;
for(edge v:e[u.id]){
if(done[v.to]) continue;
if(dis[v.to] > u.n_dis + v.w){
dis[v.to] = u.n_dis + v.w;
q.push({v.to,dis[v.to]});
pre[v.to] = u.id;
}
}
}
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int u,v,w;
cin >> u >> v >> w;
e[u].push_back({u,v,w});
}
dijkstra();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(dis[i]>=INF) cout << "-1 ";
else cout << dis[i] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
|











