codeforces 993 div4
A
题目
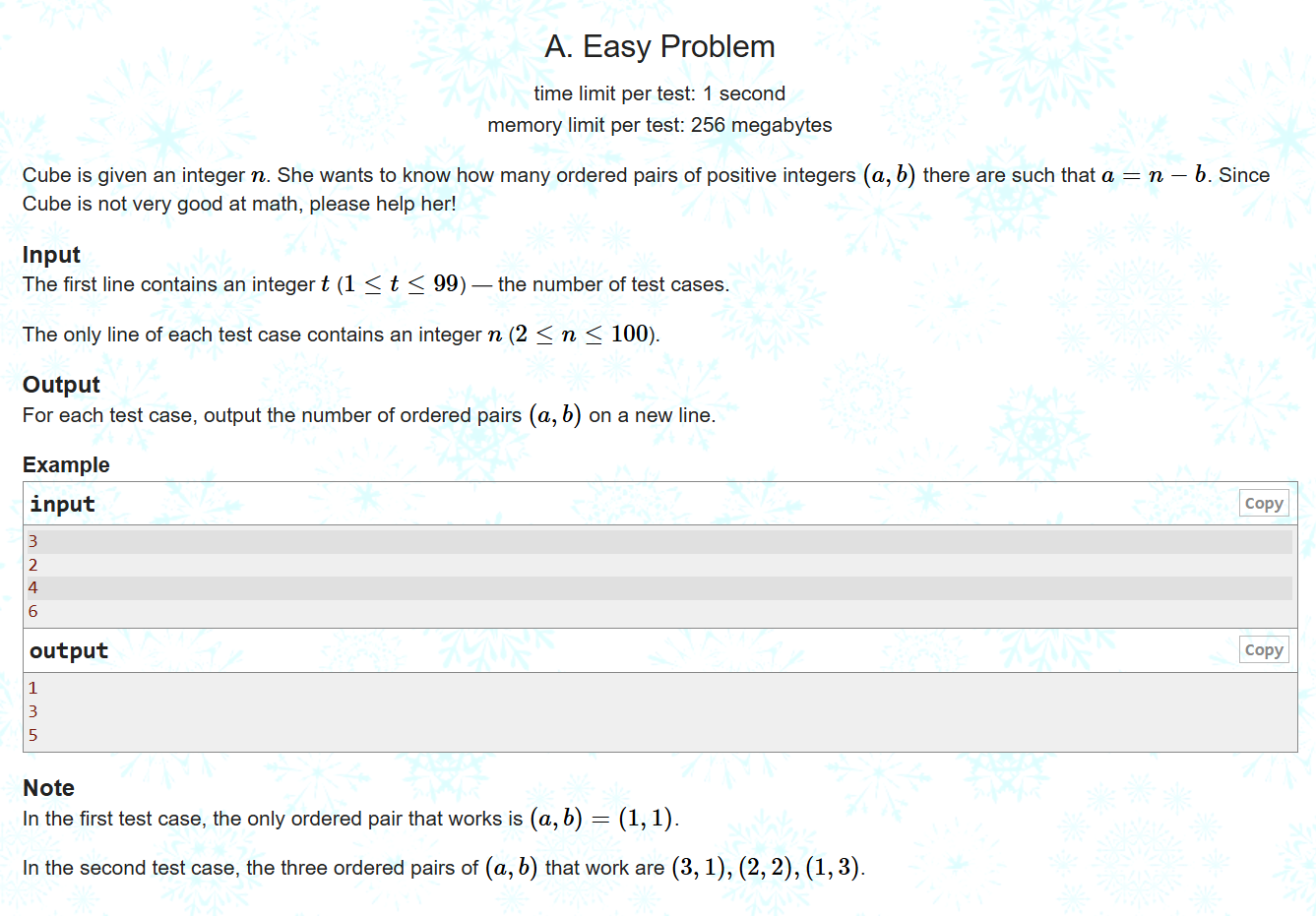
给你一个n,问你有多少有序数对(a,b)满足a+b=n?
其实就是n-1
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t,n;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> n;
cout << n-1 << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
B
题目
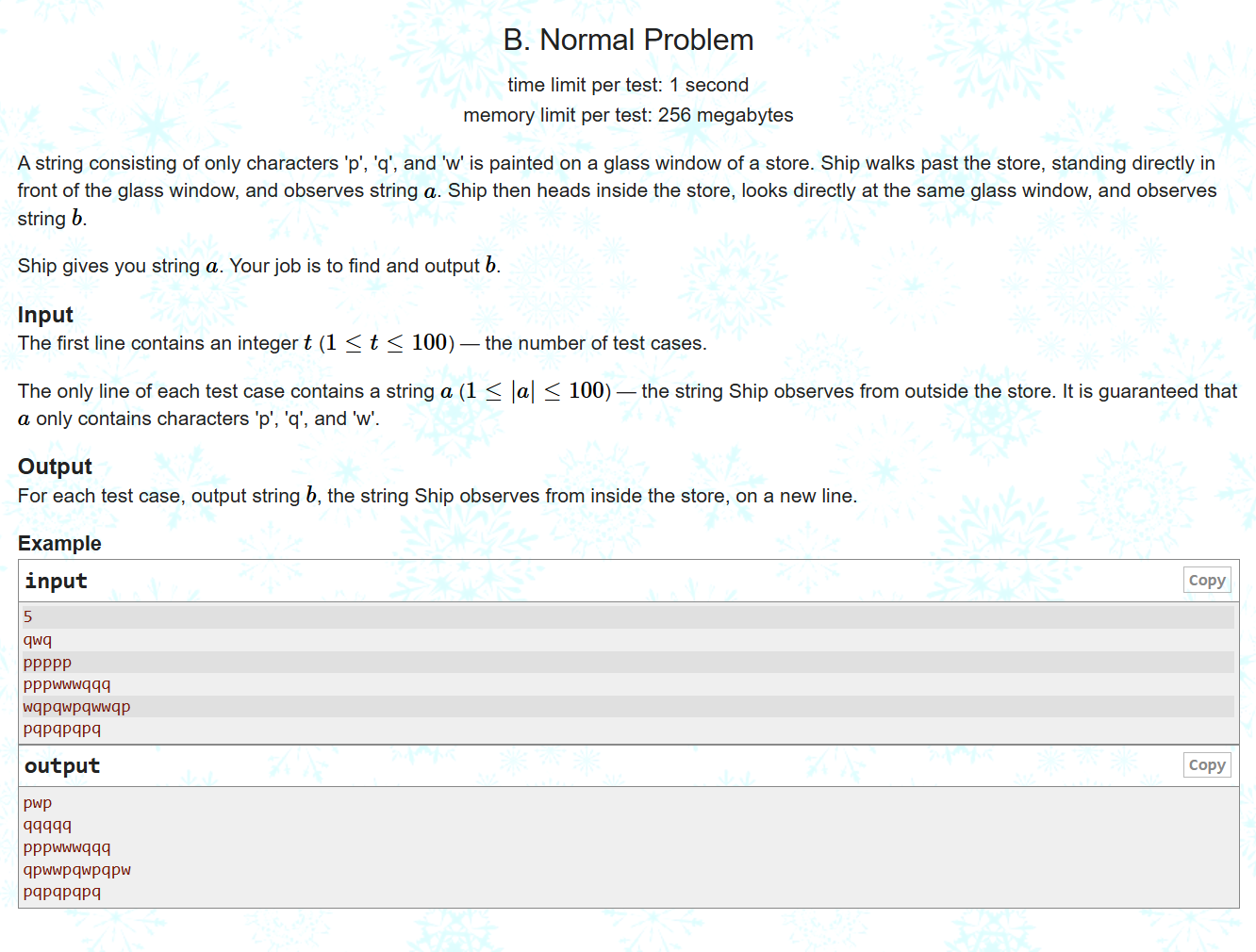
这个人在店铺外面看窗上的字母是"qwq",问你在店铺里面看窗子上是什么字母?
逆序输出,q变p,p变q,w不变
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
string s;int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> s;
for(int i=s.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
if(s[i]=='q') cout << 'p';
else if(s[i]=='p') cout << 'q';
else cout << 'w';
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
C
题目
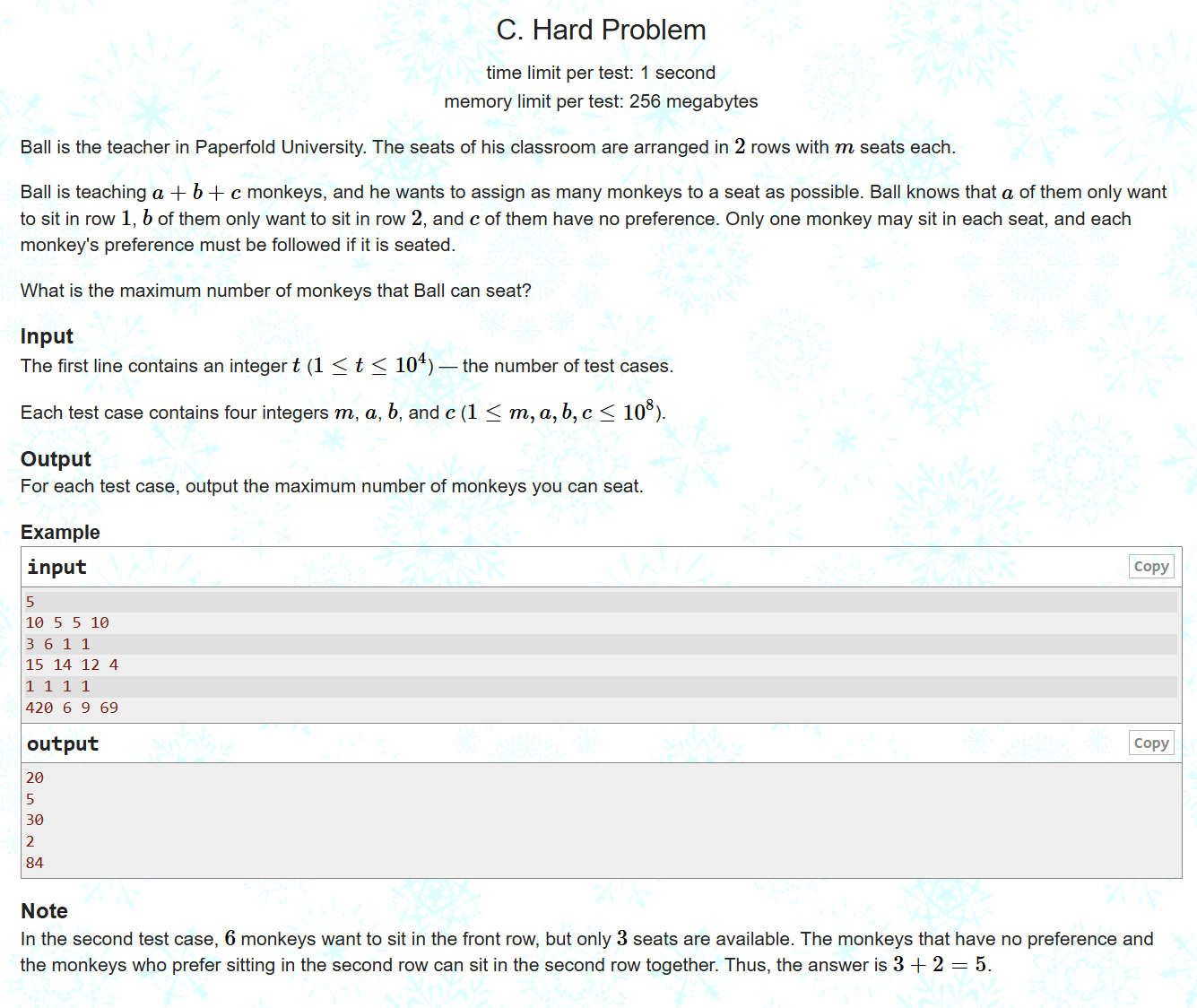
排2排座位,这两排座位总数相等。有a个人想坐第一排,有b个人想坐第二排,有c个人坐哪无所谓,但是座位是有限的,问你最多能坐多少人
这道题没有思维障碍,模拟题,用min()判断可以大幅减少代码
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t,m,a,b,c;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int res=0,z1,z2,sum=0;
cin >> m >> a >> b >> c;
z1=z2=m;
sum+=min(m,a);sum+=min(m,b);
if(m>=a) res+=m-a;
if(m>=b) res+=m-b;
sum += min(res,c);
cout << sum << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
D
题目

构造题,给出一个n(数组长度)和一个数组a,你需要构造一个数组b,使得对于每个ai(1 <= i <=n) ,在数组b的前i个数里出现次数最多
让每个数最多出现一次,这样每个数都是出现次数最多的那个数。当轮到ai的时候,如果ai已经出现过了,那么就用其他没有出现过的数来代替
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2e5+2;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int cache,Visit[maxn]={0},times=0,n;
cin >> n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin >> cache;
if(!Visit[cache]){
cout << cache << ' ';
Visit[cache]=1;
}
else times++;
}
for(int i=1;times>0;i++){
if(Visit[i]) continue;
cout << i << ' ';
times--;
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
E
题目

给你k,l1,r1,l2,r2,问你在l1<=x<=r1 , l2<=y<=r2里面有多少是满足y/x=kn的?
思维题,一开始用的枚举去做,喜提TLE
后来改用二分,找每个n下面的xmin和xmax,sum+=xmax-xmin+1,过了
注意一下二分端点的判定,我是将l-1,r+1,扩大端点。这里调试了好久
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t,k,l1,r1,l2,r2;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>k>>l1>>r1>>l2>>r2;
int k1=1,l=l1-1,r=r1+1,xmin,xmax,sum=0;
while(k1<=r2){
for(int mid;l+1<r;){
mid=(l+r)/2;
if(mid*k1<l2) l=mid;
else r=mid;
}
xmin=r,l=l1-1,r=r1+1;
for(int mid;l+1<r;){
mid=(l+r)/2;
if(mid*k1<=r2) l=mid;
else r=mid;
}
xmax=l,k1*=k,l=l1-1,r=r1+1;
sum += (xmax>=xmin?xmax-xmin+1:0);
}
cout << sum << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
牛客108
A
题目
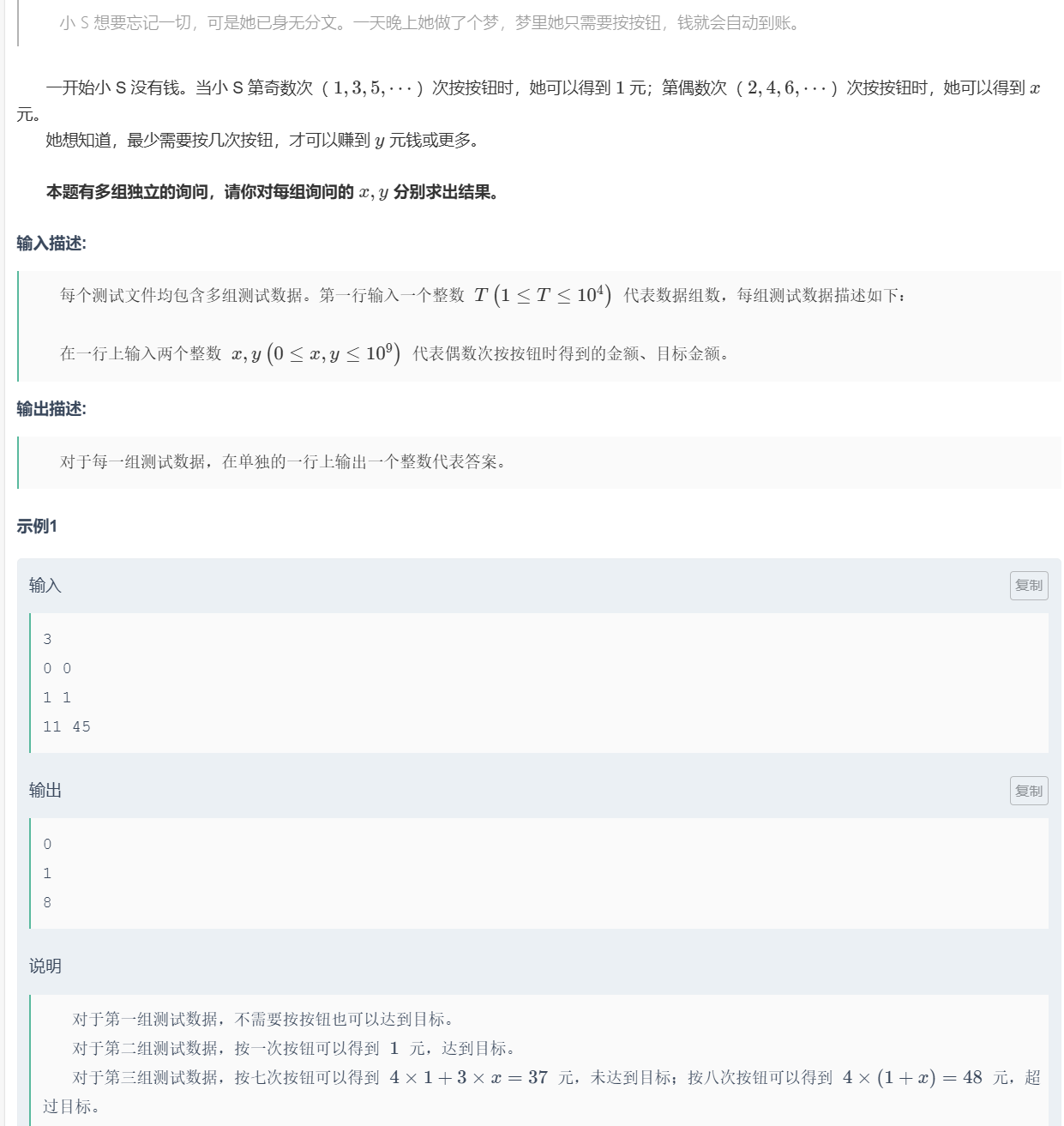
前不久才做了和这题很类似的cf的题(不是吧,牛客小白赛的A就有cf div3 B的水平了)对给的数进行处理,2个一组,先整除,再取模,对取的模进行处理
这题x、y可以等于0,有特判
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int x,y;
cin >> x >> y;
if(x==0 && y){
if(y==1) cout << 1 << '\n';
else cout << 2*(y-1)+1 << '\n';
}
else{
int sum = 1+x;
int day1 = 2*(y/sum);
if(y%sum){
int res = y%sum;
if(res==1) day1++;
else day1+=2;
}
cout << day1 << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
|
B
题目
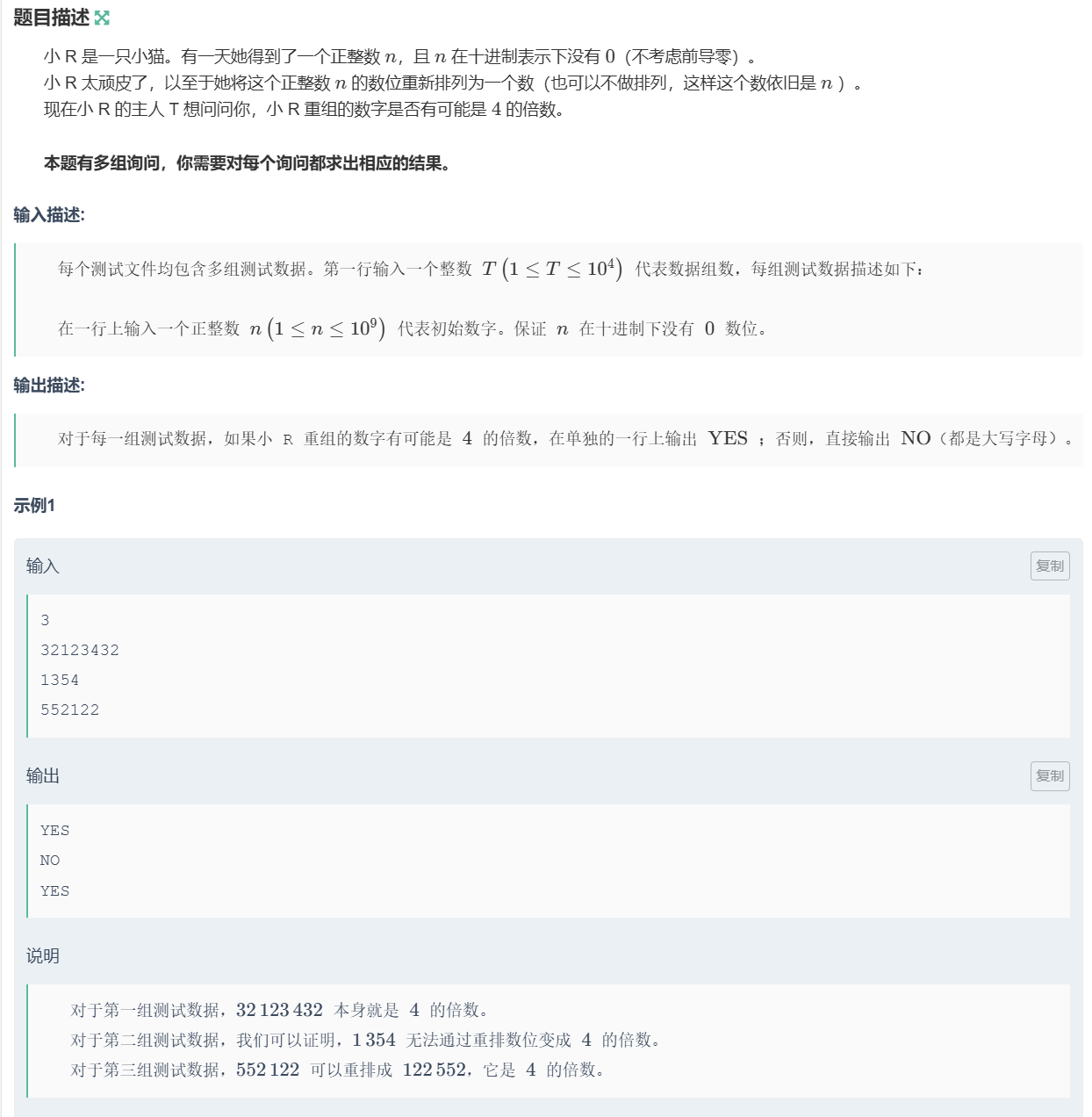
排列组合题,知道next_permutation()或者prev_permutation()以及stoi()会事半功倍
自己写字符串转数字容易tle,用stio()好些
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
string cache;
cin >> cache;
sort(cache.begin(),cache.end());
int pd=0;
do{
if((cache.back()-'0')%2) continue;
int num = stoi(cache);
pd = (num%4 ? 0:1);
}while(!pd && next_permutation(cache.begin(),cache.end()));
cout << (pd==1 ? "YES\n":"NO\n");
}
return 0;
}
|
C
题目
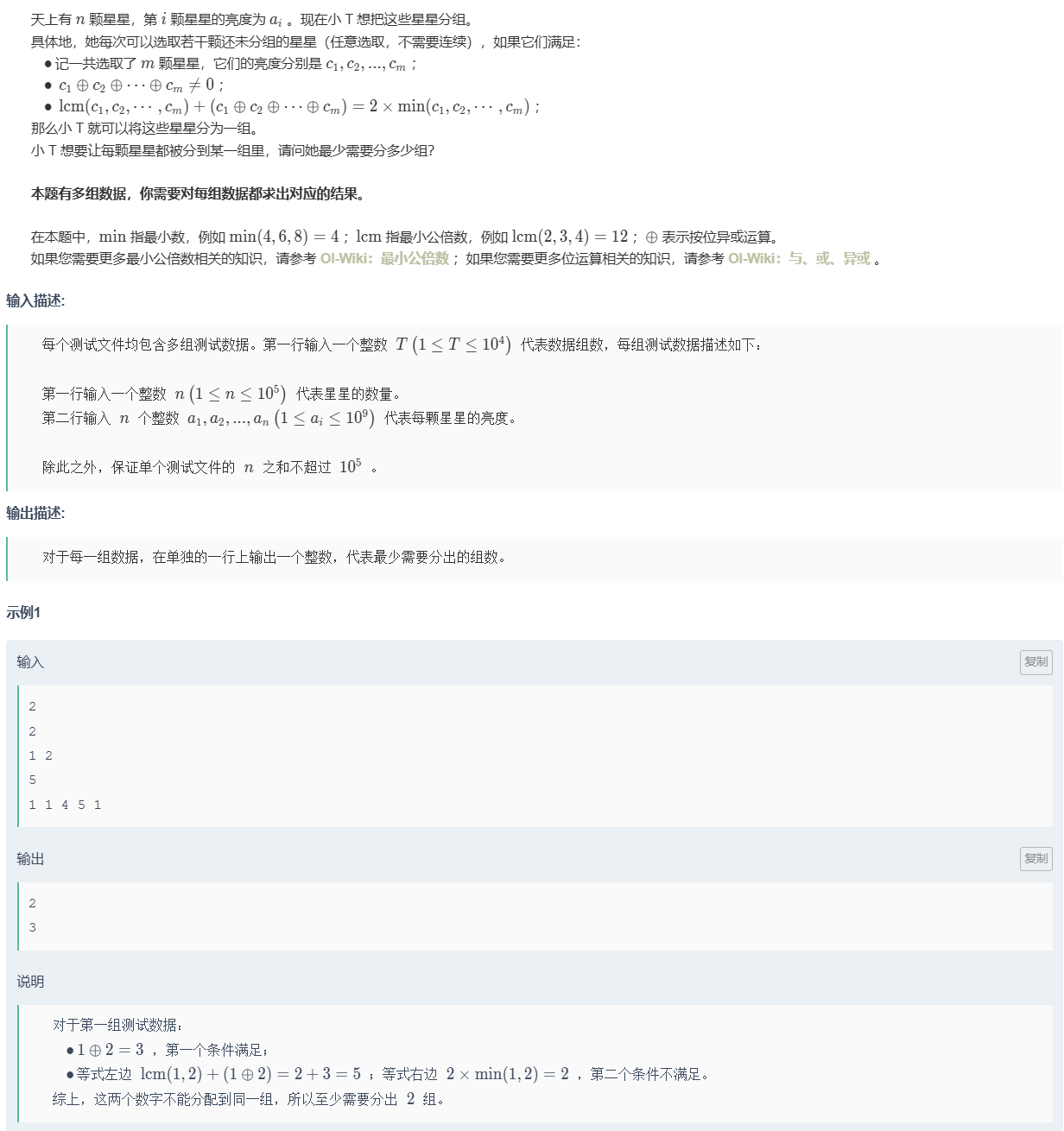
思维题,当时没开出来,看了发的题解思路后恍然大悟
第一个条件说明:异或不为0,那么一定大于零
第二个条件说明:lcm() + 一个大于零的数 =2*min(),
那么lcm() < 2*min() ①
由于lcm()一定是min()的倍数,倍数最小为2,即至少lcm() = 2*min() ②
由①和②得
所有数都相等,才能满足这俩条件
由于要异或不为0,因此某个数出现了奇数次则一定不为0,可一次删去
某个数出现了偶数次就要删两次
每个数删的次数之和 就是结果
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int n,cache,sum=0;
map <int,int> m;
set <int> s;
cin >> n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin >> cache;
m[cache]++;
s.insert(cache);
}
for(auto i:s){
if(m[i]%2) sum++;
else sum+=2;
}
cout << sum << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
D
题目
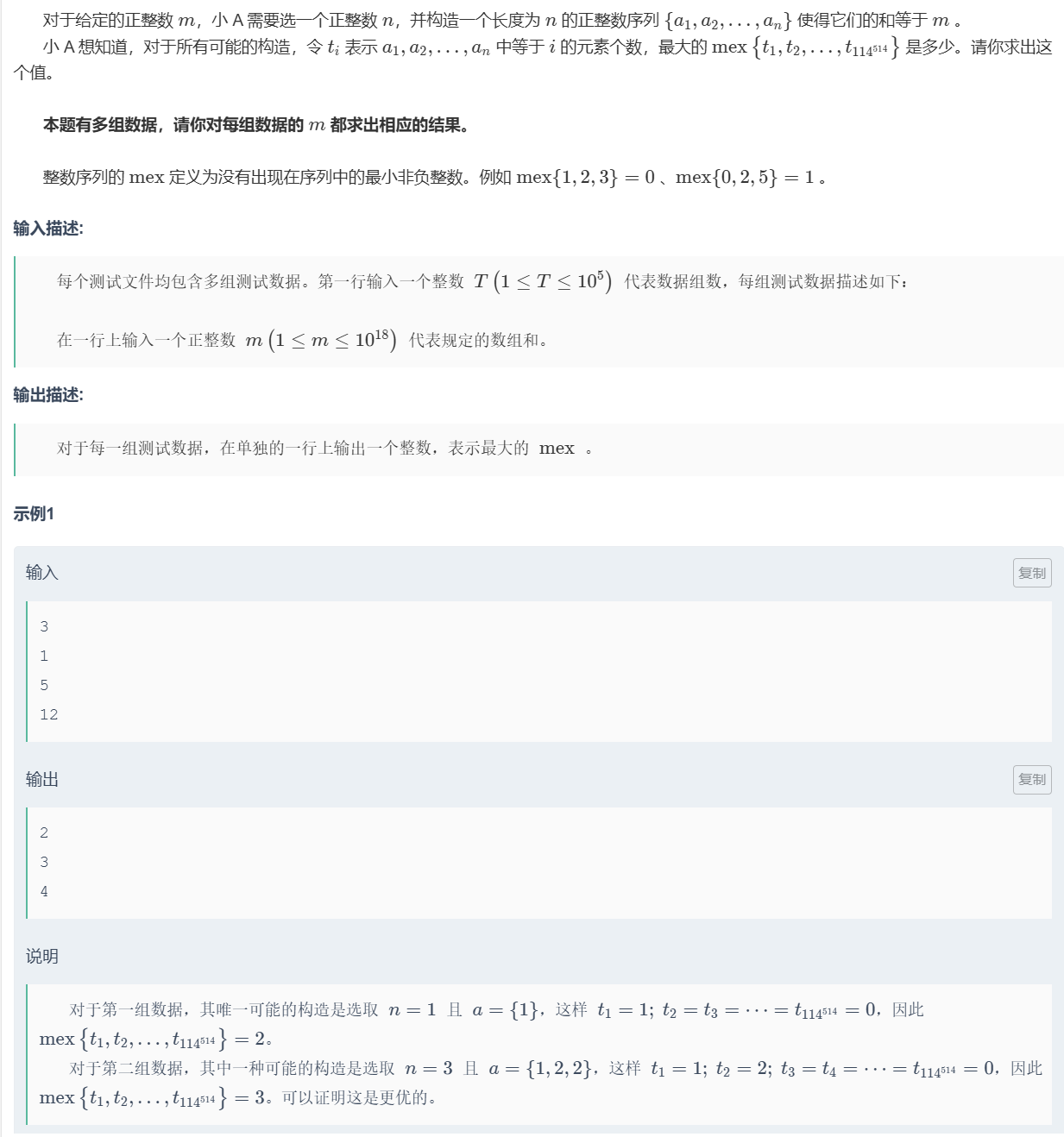
构造,根据贪心,要使得mex最大,那么越大的ti对应的i要越小,
即m >=(k^3+3k^2+2k)/6 ,输出k+1
可以用二分来找k
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define check ((mid*mid*mid+3*mid*mid+2*mid) <= 6*m)
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2e6;
int binary(int m){
int l=1,r=maxn,mid;
while(l+1<=r){
mid=(l+r+1)>>1;
if((mid*mid*mid+3*mid*mid+2*mid) > 6*m){
r=mid-1;
}
if((mid*mid*mid+3*mid*mid+2*mid) <= 6*m){
l=mid;
}
cout << '\n';
}
return l;
}
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int m,k,l,r;
cin >> m;
k=binary(m);
cout << k+1 << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
Algorithm学习
迭代加深搜索 IDDFS
当搜索树深度极深,宽度极广,DFS陷入递归无法返回、BFS队列空间直接爆炸,此时就可以采取迭代加深搜索 IDDFS
IDDFS结合了DFS和BFS。迭代过程上,在每一层的广度上采用了BFS,在具体实现上是DFS,大概的操作是:
- 先设定搜索深度为1,用DFS搜索到第1层即停止。也就是说,用DFS搜索一个
深度为1的搜索树。
- 如果没有找到答案,再设定深度为2,用 DFS 搜索前两层即停止。也就是说,用
DFS搜索一个深度为2的搜索树。
- 继续设定深度为3、4……逐步扩大 DFS的搜索深度,直到找到答案。
埃及分数可用IDDFS来解决
题目

该题的搜索树深度和宽度都可能是无穷的,所以要用IDDFS
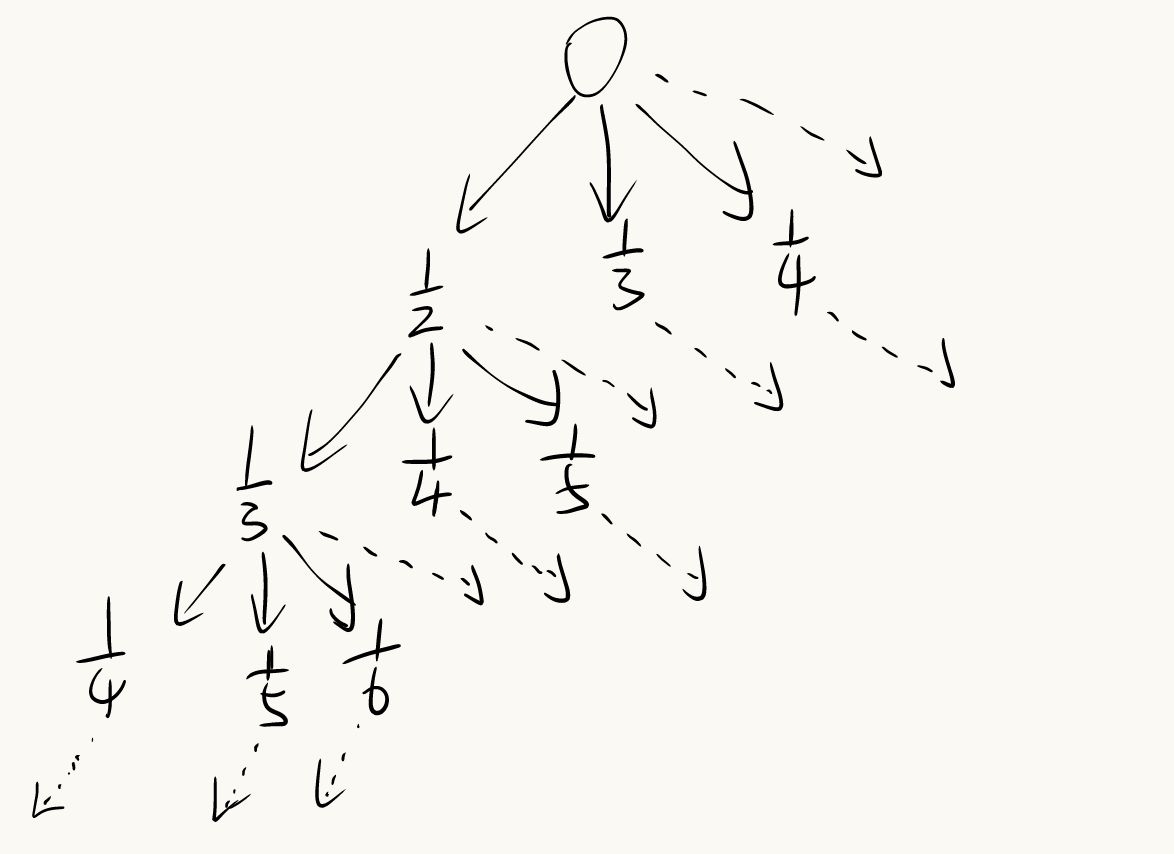
这一层找到了就不会去下一层找了,所以ans和temp的分母数量是相同的,也就是该层的层数
每一层搜索分母的起始值为i=b/a+1,i是分母,+1是因为找的分数要比题目给的分数小
每一层搜索分母的时候也有个限度,不可能无限搜吧,这个限度就是:
如果 剩余分母个数/分母 < 题目给的分数 ,即(deep-d+1)/i < a/b,那么这层就不用搜了,因为这层剩下的分数之和的最大值就是(deep-d+1)/i,如果这小于a/b了,那么这层分数再怎么累加也比a/b小。可以放缩证明,证明如下:

代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e7;
int ans[maxn+2],temp[maxn+2],pd=0,deep;
int gcd(int a,int b){
return (b==0 ? a:gcd(b,a%b));
}
void simp(int &a,int &b){
int gys=gcd(a,b);
a=a/gys;
b=b/gys;
}
void iddfs(int a,int b,int d){
if(d==deep){
if(b%a) return;
if(temp[deep-1]==b/a) return;
pd=1;
temp[d]=b/a;
int pd1=0;
if(ans[d]>temp[d]) memcpy(ans,temp,sizeof(int)*(d+1));
return;
}
for(int i=max(temp[d-1]+1,b/a+1);;i++){
if(b*(deep-d+1)<a*i) break;
temp[d]=i;
int a_1=a*i-b,b_1=b*i;
simp(a_1,b_1);
iddfs(a_1,b_1,d+1);
}
}
signed main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
simp(a,b);
if(!b%a) cout << b/a << '\n';
else{
for(deep=2;;deep++){
ans[1]=0,ans[deep]=maxn;
iddfs(a,b,1);
if(pd) break;
}
for(int i=1;i<=deep;i++) cout << ans[i] << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
最小公倍数
先求最大公约数gcd(a,b)
1
2
3
| int gcd(int a,int b){
return b==0 ? a : gcd(b,a%b);
}
|
,最小公倍数lcm(a,b)与其的关系为:
gcd(a,b)*lcm(a,b)=a*b
因此lcm(a,b)=(a*b)/gcd(a,b)
1
2
3
| int lcm(int a,int b){
return a/gcd(a,b)*b;
}
|
高精度
C++不像Java那样处理高精度非常简单,C++最大数据类型只有64位,如果要处理更大的数,只能用数组来模拟。
高精度算法本质上是用字符串模拟数字进行计算,再利用类似于数学里的竖式的形式,一位一位进行相关计算
读取数字,转为数组:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| void read(int a[]) {
string s;
cin >> s;
len = s.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
a[i] = s[len-1-i] - '0';
}
|
进位、借位
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
if(c[i] >= 10) {
c[i] -= 10;
c[i+1]++;
}
if(a[i] < b[i]) {
a[i+1]--;
a[i] += 10;
}
x = c[i + j - 1] / 10;
c[i + j - 1] % 10;
|
高精度加法
从最低位开始,两加数相加,如果大于等于10,则高位++,该位-10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| void clear(int a[]){
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) a[i] = 0;
}
void add(int a[], int b[], int c[]){
clear(c);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
c[i] += a[i] +b [i];
if(c[i] >= 10) {
c[i] -= 10;
c[i+1]++;
}
}
}
|
高精度减法
从最低位开始,两加数相减,如果小于0,则高位–,该位+10
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| void clear(int a[]){
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) a[i] = 0;
}
void sub(int a[], int b[], int c[]){
clear(c);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
c[i] += a[i] - b[i];
if(c[i] < 0){
c[i] += 10;
c[i+1] --;
}
}
}
|
这里需要注意,sub(a,b,c)只能处理a>b的情况,如果b>a的话需要另判,以下是完整的高精度减法代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a1,b1,pd=0,pd1=0;
void read(int a[]){
string s;
cin >> s;
if(pd) a1=stoi(s),pd=1;
else b1=stoi(s);
int len=s.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
a[i] = s[len-1-i] -'0';
}
void sub(int a[],int b[],int c[]){
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
c[i] += a[i]-b[i];
if(c[i]<0){
c[i+1]--;
c[i]+=10;
}
}
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int a[3]={0},b[3]={0},c[3]={0};
read(a);read(b);
if(a1>b1) sub(a,b,c);
else{
sub(b,a,c);pd1=1;
}
if(pd1) cout << '-';
for(int i=2;i>=0;i--){
if(!c[i] && i!=0) continue;
cout << c[i];
}
return 0;
}
|
高精度乘法
高精度 * 高精度 分解为 高精度 * 单精度,再进行计算。
这里直接计算结果中的从低到高第 i 位,且一并处理了进位,第 i 次循环为 c[i] 加上了所有满足 p + q = i 的 a[p] 与 b[q] 的乘积之和,更为简短
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| void mul(int a[], int b[], int c[]) {
clear(c);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++)
c[i]+= a[j] * b[i-j];
if(c[i] >= 10){
c[i+1] += c[i] / 10;
c[i] %= 10;
}
}
}
|
高精度除法
高精度除法可以模拟竖式除法,看作一个逐次减法的过程
这里得到被除数的长度la与除数的长度lb,从下标la-lb开始,从高位到低位来计算商,减少了冗余运算。 被除数 a 以下标 last_dg 为最低位,是否可以再减去除数 b 而保持非负
,len 是除数 b 的长度,避免反复计算
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
bool greater_eq(int a[], int b[], int last_dg, int length){
if(a[last_dg+length] != 0) return true;
for(int i = length-1;i>=0;i--){
if(a[last_dg+i] > b[i]) return true;
if(a[last_dg+i] < b[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
void div(int a[], int b[], int c[], int d[]){
clear(c);
clear(d);
int la, lb;
for(la=len-1;la>0;la--)
if(a[la-1] != 0) break;
for(lb=len-1;lb>0;lb--)
if(b[lb-1] != 0) break;
if(lb==0){
puts("NO");
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<la;i++) d[i] = a[i];
for(int i=la-lb;i>=0;i--){
while(greater_eq(d, b, i, lb)){
for(int j=0;j<lb;j++){
d[i+j] -= b[j];
if(d[i+j] < 0){
d[i+j+1] -= 1;
d[i+j] += 10;
}
}
c[i] += 1;
}
}
}
|
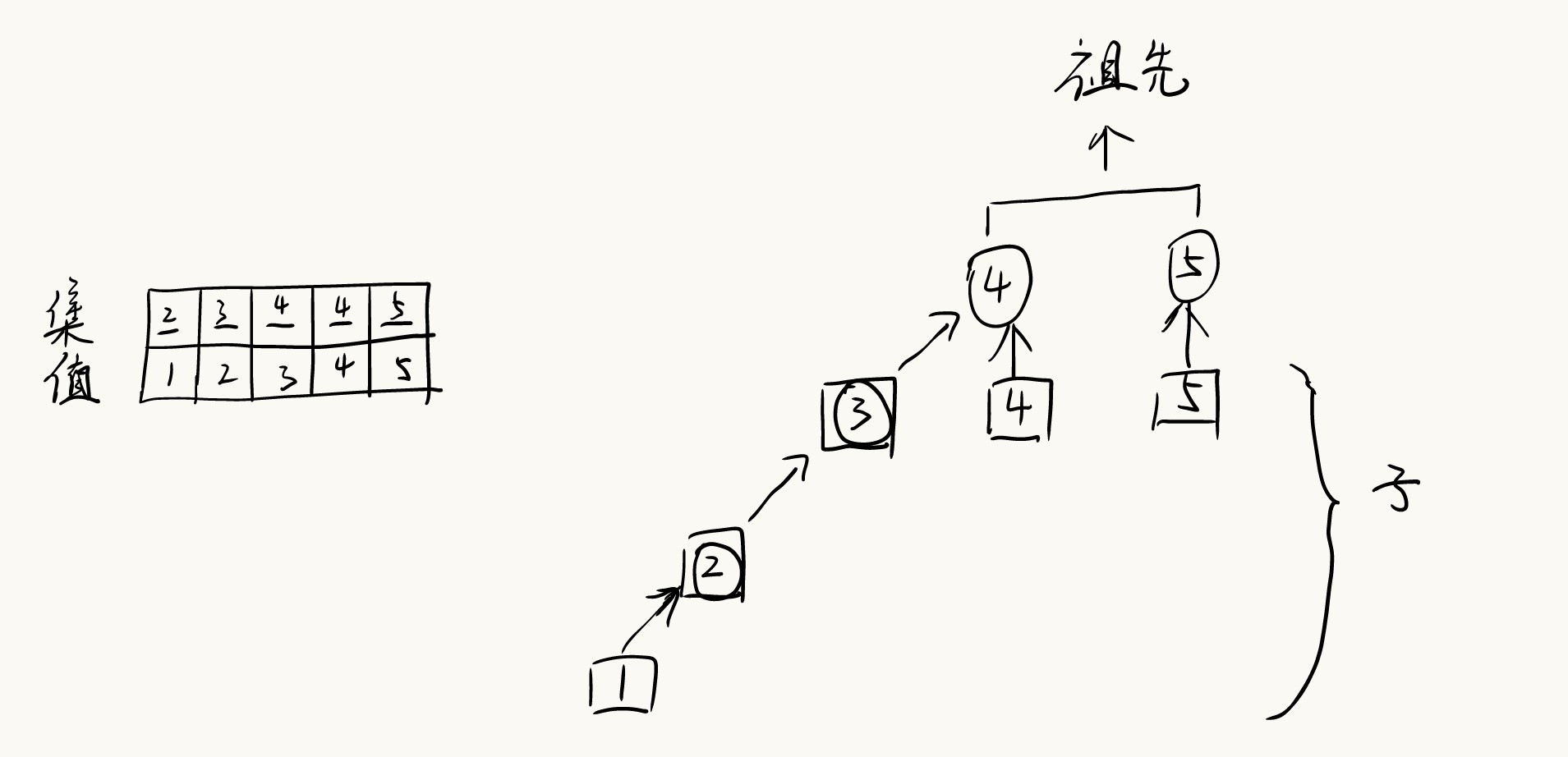
并查集
将编号分别为1~n的n个对象划分为不相交集合,在每个集合中,选择其中某个元素代表所在集合。在这个集合中,并查集的操作有初始化,合并,查找。
合并:合并两个元素所属集合(合并对应的树)
查询:查询某个元素所属集合(查询对应的树的根节点,也就是祖先),这可以用于判断两个元素是否属于同一集合
用并查集的基础操作完成HDU 1213
题目
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int s[1005];
int find_s(int x){
return (x==s[x] ? x:find_s(s[x]));
}
void union_s(int a,int b){
int x=find_s(a),y=find_s(b);
if(x!=y) s[x]=s[y];
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
int n,m,a,b,sum=0;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i=0;i<1005;i++) s[i]=i;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
cin >> a >> b;
union_s(a,b);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(s[i]==i) sum++;
cout << sum << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
路径压缩
在合并过程中,树可能会发生退化,退成链表,增加查询的时间复杂度。通过路径压缩,将所有的子节点直接连到根节点,可大幅缩短搜索路径,加快查询
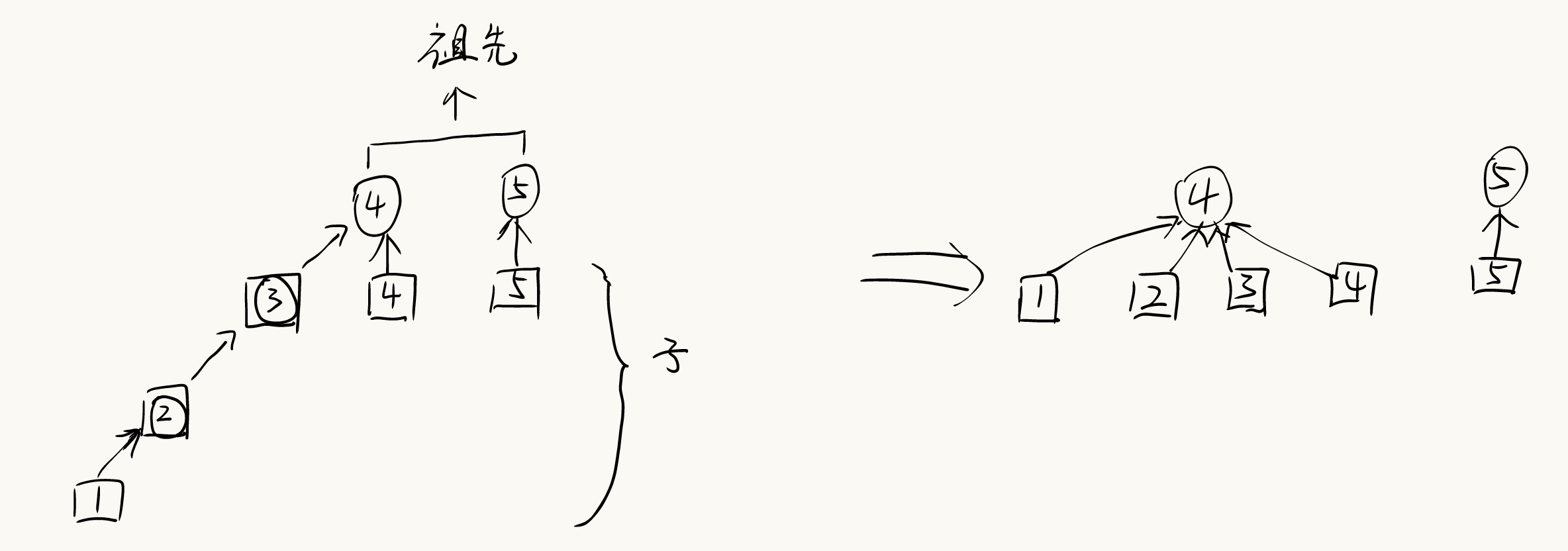
1
2
3
| int find_s(int x){
return (x==s[x] ? x : s[x]=find_s(s[x]));
}
|





















