codeforces 988 div.3
A
题目
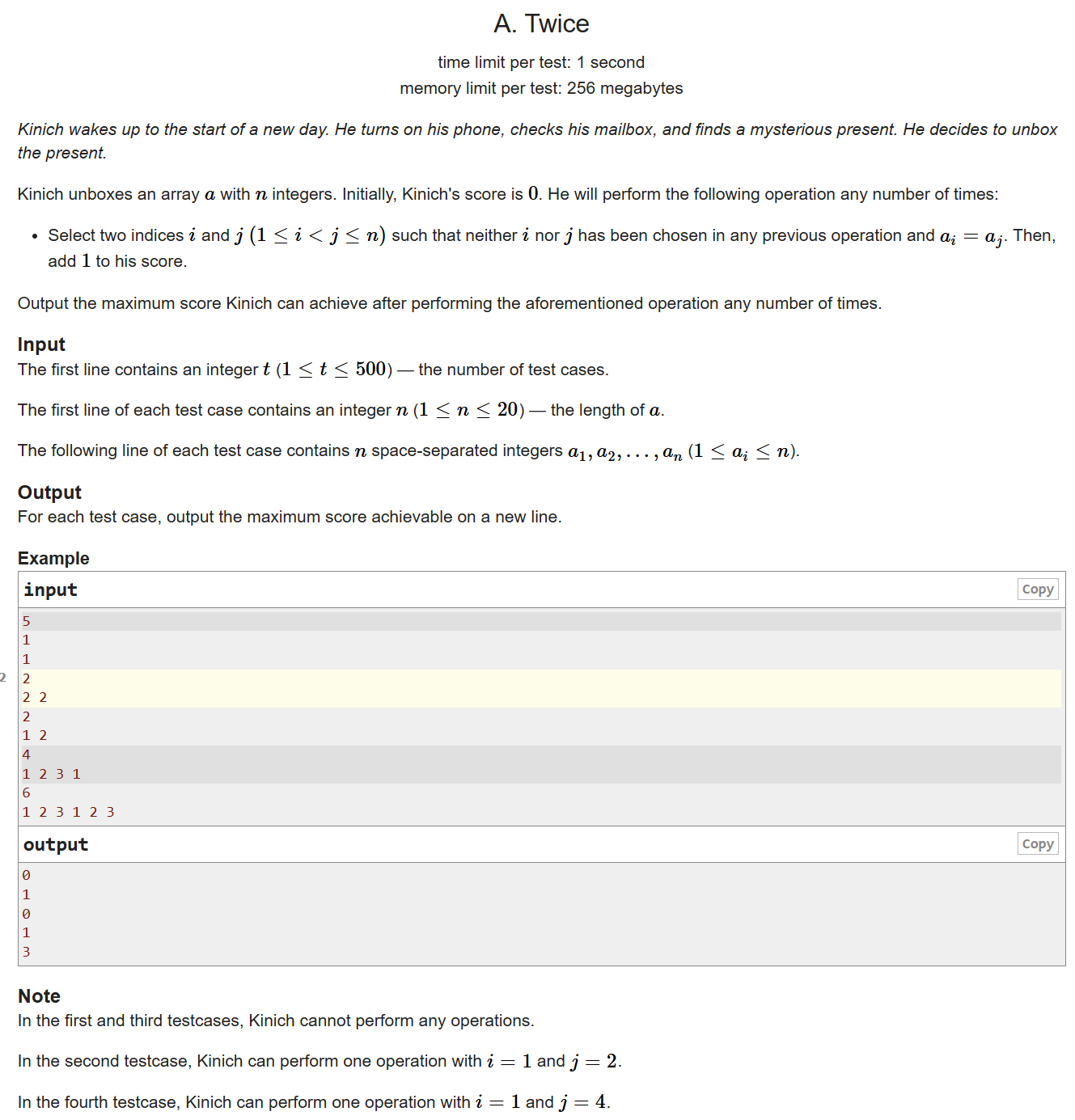
找相同的数字,有点像天天爱消除,两个相同的数字就可以消掉,用个数组记录数字出现的次数就ok。这题数据很小,什么方法都行
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int t,score,n,cache,a[21 ]; int main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); cin >> t; while (t--){ cin >> n; fill_n (&a[0 ],21 ,0 );score=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ cin >> cache; a[cache-1 ]++; } for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ while (a[i]>1 ){ a[i] -= 2 ; score++; } } cout << score << '\n' ; } return 0 ; }
B
题目
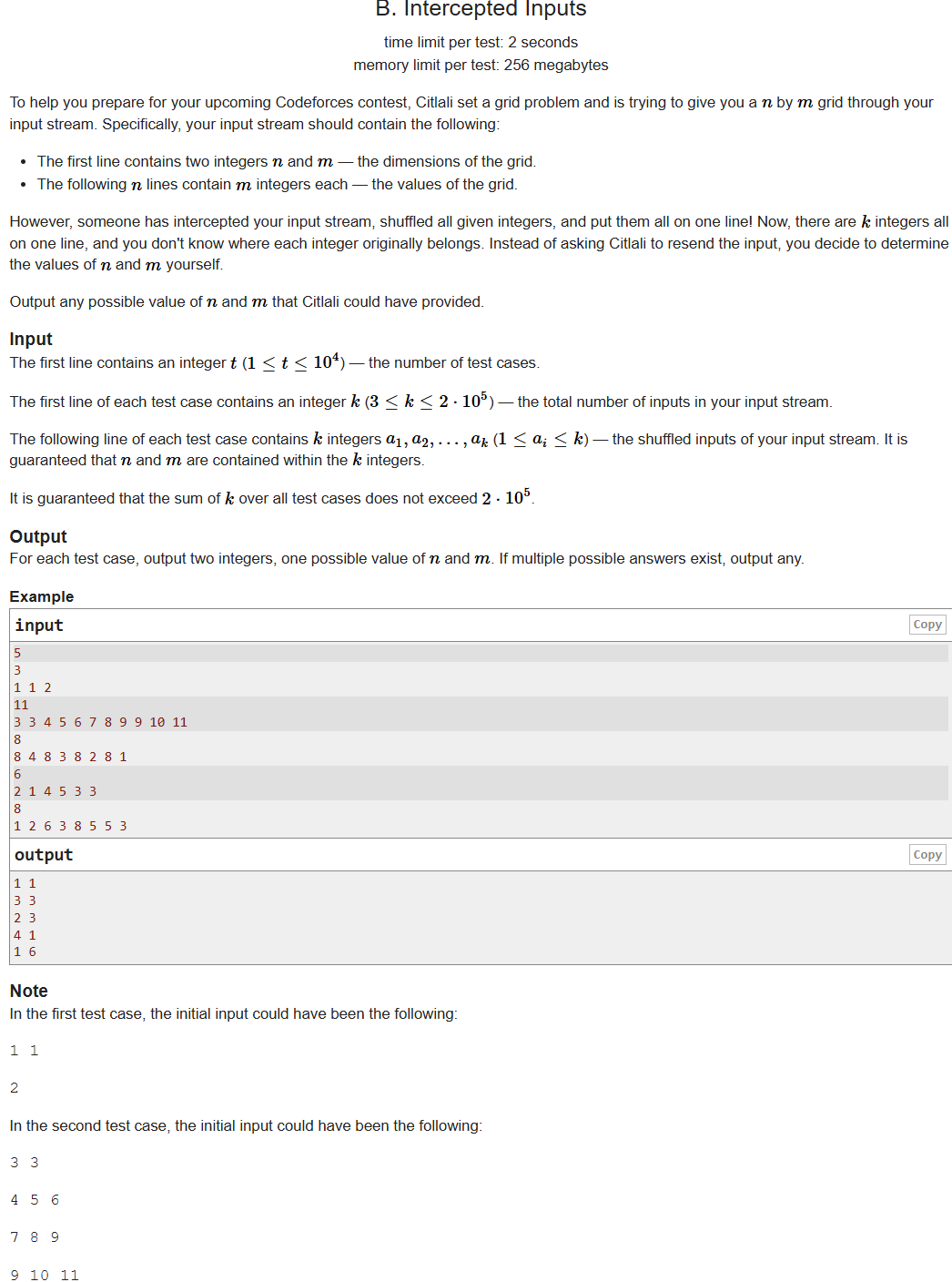
挺像因数分解,当碰到x分解出来的两个因数都在数组a里,那么就输出
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int t,k,cache;int main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); cin >> t; while (t--){ cin >> k; int a[200010 ]={0 },len=k-2 ; for (int i=0 ;i<k;i++){ cin >> cache; a[cache]++; } for (int i=1 ;i<=sqrt (len);i++){ if (len%i!=0 ) continue ; else if (i==len/i && a[i]>1 ){ cout << i <<' ' << i <<endl;break ; } else if (a[i]!=0 && a[len/i]!=0 ){ cout << i <<' ' << len/i <<endl;break ; } } } return 0 ; }
C
题目
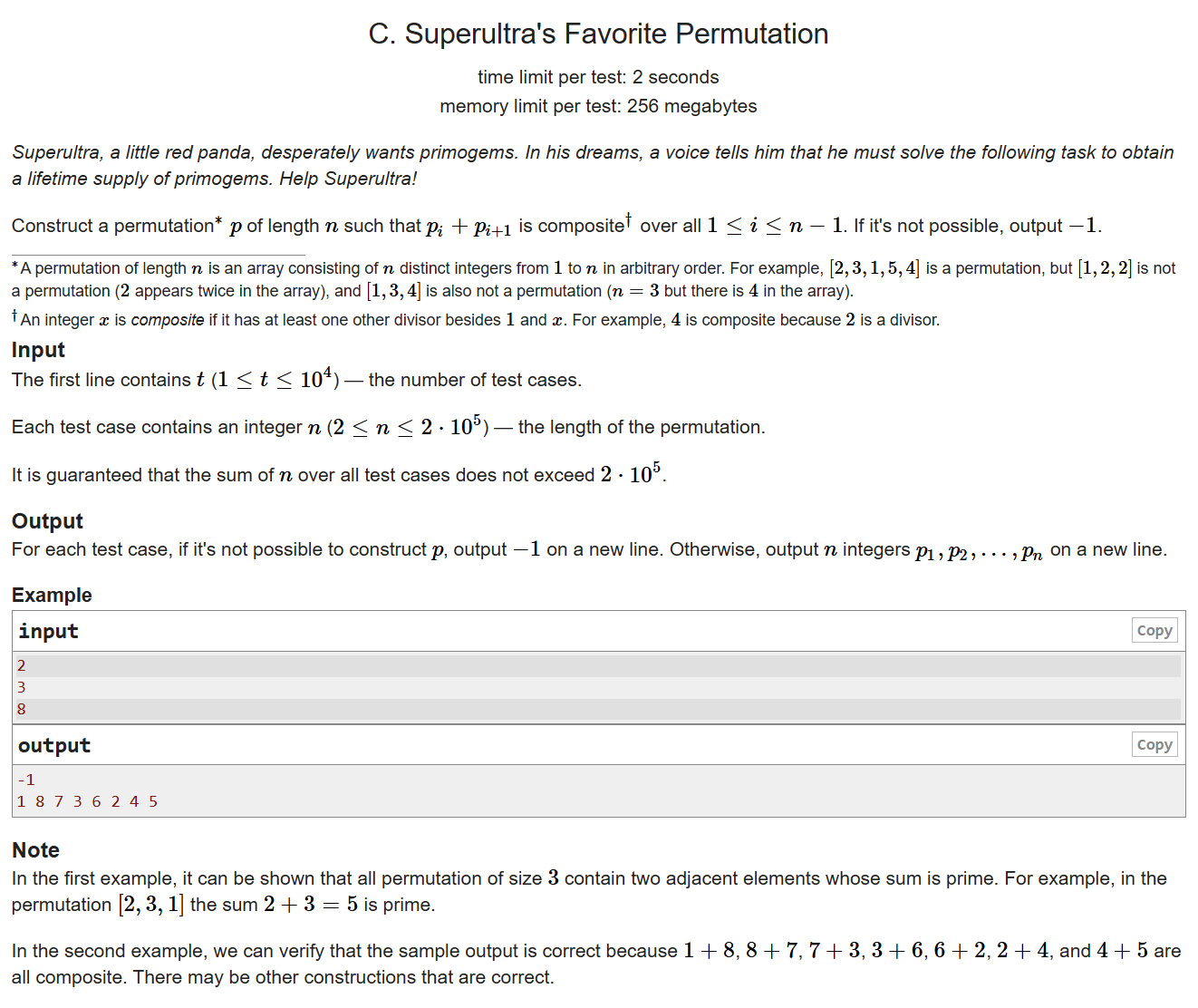
给一个n,求出从1到n中所有排列里 相邻两数之间是合数的排列。
:::warning
奇+奇=偶 偶+偶=偶 除2以外的偶都是合数
:::
n<=4绝对无解,n>4时最小的奇偶组合是5、4,因此奇数放左边,中间是5、4,偶数放右边
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int t,n;int main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); cin >> t; while (t--){ cin >> n; if (n<5 ){ cout << -1 << '\n' ;continue ; } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i+=2 ){ if (i==5 ) continue ; cout << i <<' ' ; } cout << 5 << ' ' << 4 <<' ' ; for (int i=2 ;i<=n;i+=2 ){ if (i==4 ) continue ; cout << i << ' ' ; } cout << '\n' ; } return 0 ; }
D
题目
微信爆款小游戏“跳一跳”的魔改版。初始跳跃能力是1,路上会有“跳跃能量包”,可以加一些跳跃距离,你可以舔包或者不舔。你一次可以跳跃1~最远跳跃距离。某些区间是障碍,你要跳过障碍。问你从起点跳到终点所徐舔的最少包数,到不了终点就输出-1。
有点复杂,判断每个障碍区间能不能跳过去,当能量包的刷新地点在这段障碍区间之后就把能量包先存进栈里,判断完后再取出来。由于问的是最少包数,所以要用priority_queue(小根堆)来
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long #define len block[i].r-block[i].l+2 using namespace std;int t,n,m,l;struct z { int l,r; }block[200005 ]; struct e { int x,v; }energy[200005 ]; signed main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); cin >> t; while (t--){ cin >> n >> m >> l; int skip=1 ,sum=0 ,pd=1 ; priority_queue <pair<int ,int >,vector<pair<int ,int >>,less<pair<int ,int >>> q; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++) cin >> block[i].l >> block[i].r; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ cin >> energy[i].x >> energy[i].v; q.push ({energy[i].v,energy[i].x}); } for (int i=0 ;i<n & pd;i++){ stack <pair<int ,int >> s; while (!q.empty ()){ if (skip>=len) break ; if (q.top ().second > block[i].l){ s.push (q.top ());q.pop (); } else { skip += q.top ().first;q.pop (); sum++; } } if (skip < len){ pd=0 ; break ; } while (!s.empty ()){ q.push (s.top ());s.pop (); } } cout << (pd==1 ? sum:-1 ) <<'\n' ; } return 0 ; }
SCU 24.12.15
E
题目
比赛的时候用双指针做的。
非常奇怪,比赛时我把几个变量声明为long long类型,奶奶的 怎么也过不了,
比赛结束后我直接#define int long long,奶奶的 居然过了,不明白为什么,下来查查
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;int n,cache,a[100005 ],sum=0 ;signed main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); fill_n (&a[0 ],100005 ,202412150 ); cin >> n; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ cin >> cache; a[i]=cache; } if (n==1 || n==2 ) cout << (n==1 ? 1 :3 ) << '\n' ; else { long long cha=a[2 ]-a[1 ]; for (int l=1 ,r=2 ;l<=n;){ if (cha == a[r]-a[r-1 ]){ r++; } else { sum += (r-l+1 )*(r-l)/2 - (r-l) - (r-l-1 ); l=r-1 ;cha=a[r]-a[l]; } } cout << sum+n+n-1 << '\n' ; } return 0 ; }
G
题目
埃氏筛打表,输出n后查表
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int MAXN = 1e6 +5 ;vector <int > prime; bool Visit[MAXN];void sushu (int n) for (int i=2 ;i*i<=n;i++){ if (!Visit[i]) for (int j=i*i;j<=n;j+=i) Visit[j]=true ; } for (int i=2 ;i<=n;i++) if (!Visit[i]) prime.push_back (i); } int main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); sushu (MAXN); int t,n; cin >> t; while (t--){ cin >> n; cout << distance (prime.begin (),upper_bound (prime.begin (),prime.end (),n))+1 << '\n' ; } return 0 ; }
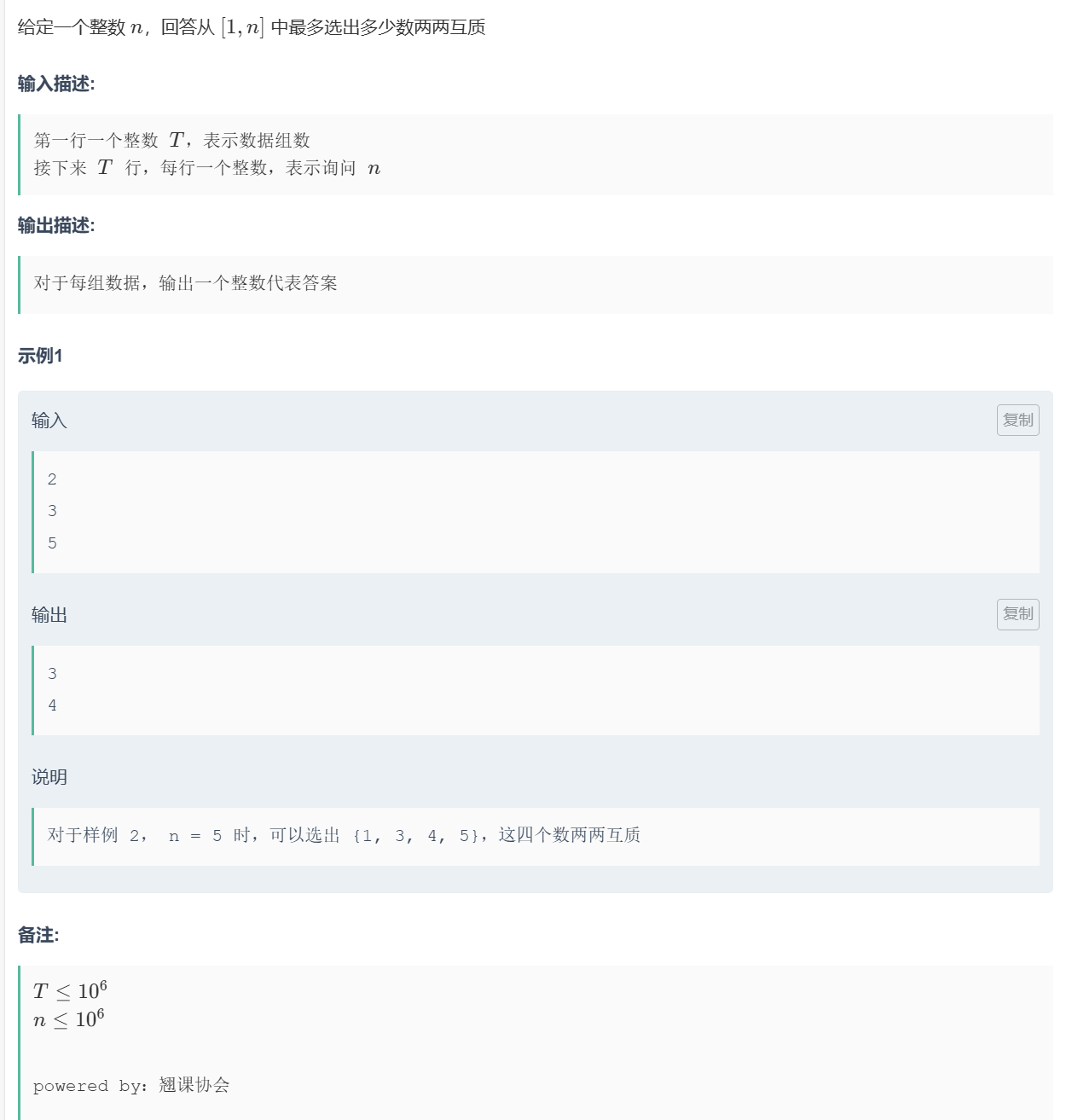
K
题目
二分找最小初始容量,球能进箱子就进箱子,箱子满了进公共容器,公器–。每回合公器++,如果公共容器能一直>0就return 1,否则0
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int a[10002 ],b[10002 ],n;int football (int m) int ai=m,bi=m,residual=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ residual++; ai-=a[i],bi-=b[i]; if (ai<0 ) residual+=ai,ai=0 ; if (bi<0 ) residual+=bi,bi=0 ; if (residual<0 ) return 0 ; } return 1 ; } int main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); int t; cin >> t; while (t--){ cin >> n; int l=0 ,r=1e9 ,ans; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++) cin >> a[i] >> b[i]; while (l<=r){ int mid=(l+r)/2 ; if (football (mid)) r=mid-1 ,ans=mid; else l=mid+1 ; } cout << ans << '\n' ; } return 0 ; }
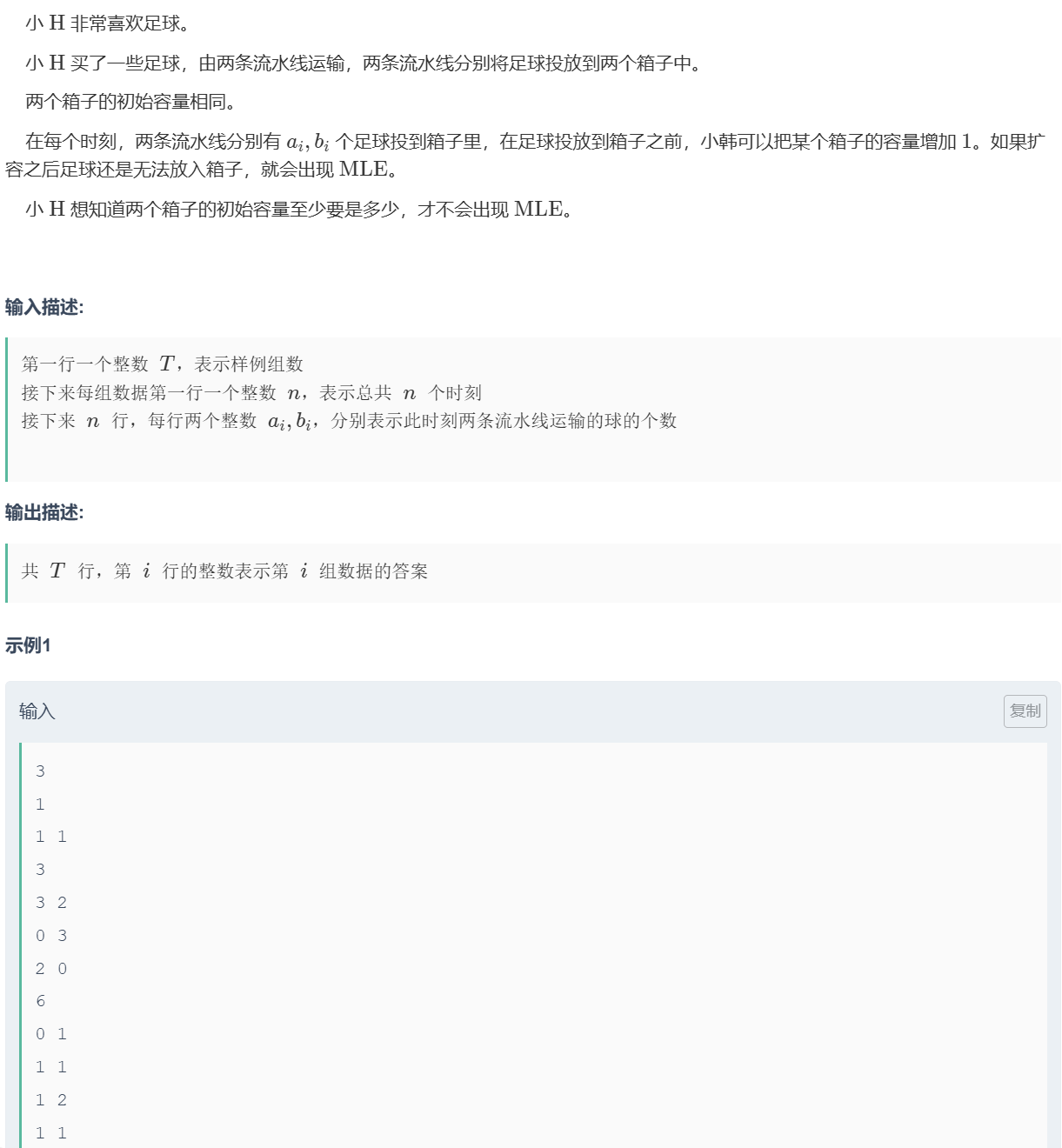
H
题目
由瞪眼法可知,对于任意一个数n,在[2/n,n] (或[2/n+1,n]) 的任意两个数是不能构成大于1的倍数关系的,也就不能整除。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); int t,n,len=0 ; cin >> t; while (t--){ cin >> n; len = n%2 ==0 ?n/2 :n/2 +1 ; cout << len << '\n' ; for (int i=n/2 +1 ;i<=n;i++) cout << i << ' ' ; cout << '\n' ; } return 0 ; }
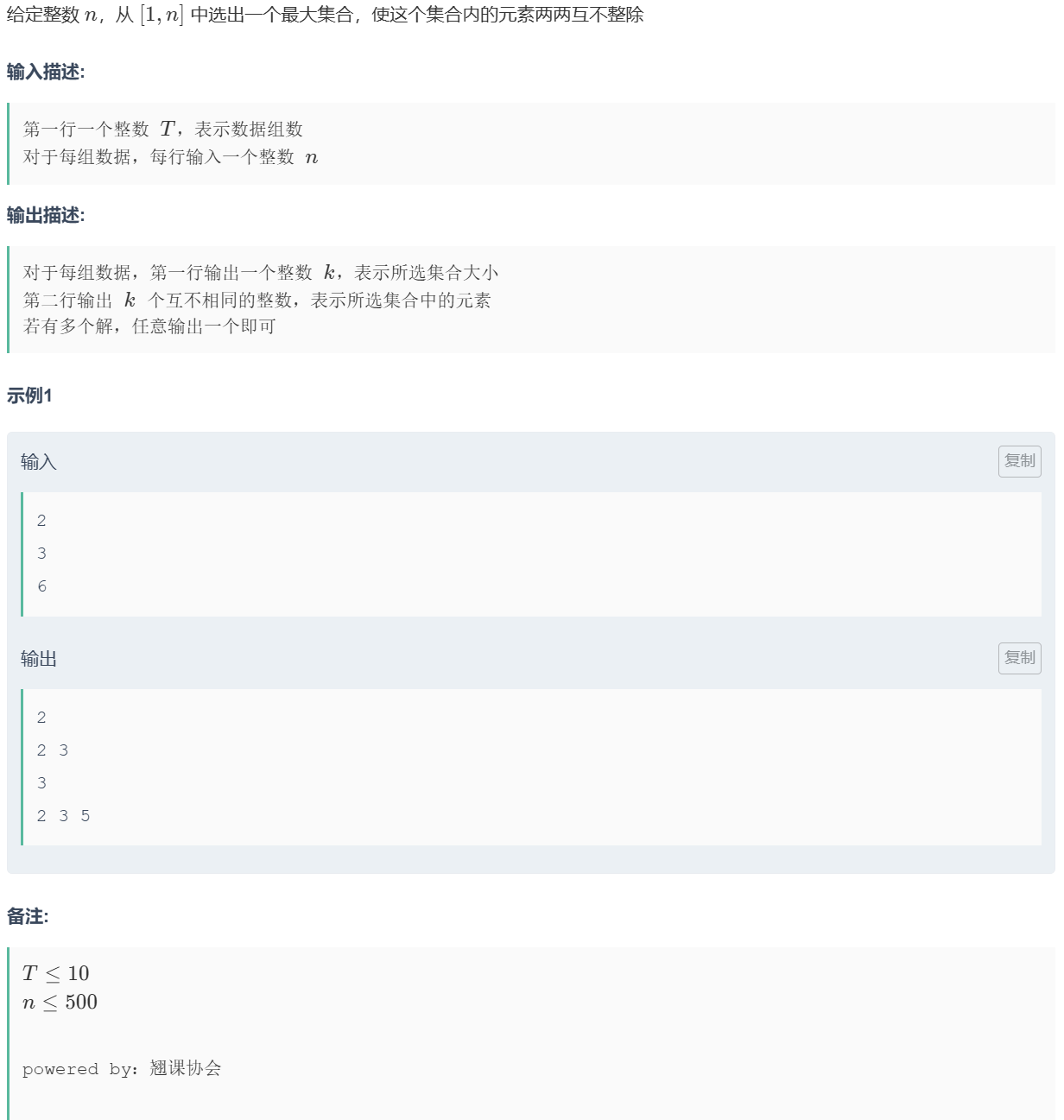
I
题目
这就是川大的数学题吗(qwq)。
先打表,把2的次幂数全部储存。
给出区间 [L,R],用while循环找到最大的 2 k ≤R,此时 [2 k , R ]数字全选,而区间[2 k +1−R,2 k −1]的数字全不选,这是一次选择,令k–就可以进行下一次选择,能进行选择的条件是l<=r && k>=0
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;const int maxn = 2 *(1e18 )+2 ;vector <int > cimi; void dabiao () for (int i=1 ;i<=maxn;i*=2 ) cimi.push_back (i); } signed main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); dabiao (); int t,l,r; cin >> t; while (t--){ int sum=0 ,k=0 ; cin >> l >> r; while (cimi[k+1 ]<=r) k++; while (l<=r && k>=0 ){ if (cimi[k]<=r){ sum += r-max (cimi[k],l)+1 ; r = cimi[k]-(r-cimi[k]+1 ); } k--; } cout << sum << '\n' ; } return 0 ; }
Algorithm
A*
A 相当于 BFS+贪心 *,是最短路里比较简单的一种算法。A通常与曼哈顿距离 扯上联系。曼哈顿距离:两个点在标准坐标系上的实际距离,也称为出租车距离 。A 算法的一般性描述:在搜索过程中,用一个评估函数 对当前情况进行评估,得到最好的状态,从这个状态继续搜索,直到目标。
以下是用A*算法来实现的八数码。manhadun()是评估函数了,来评估某个状态里的每个数距离它的最终位置的距离之和,并把这个距离之和和这个状态对应的步数存进优先队列(小根堆)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;string goal="123804765" ,start; int explore[][2 ]={0 ,1 ,0 ,-1 ,1 ,0 ,-1 ,0 },nextx,nexty,goer[][2 ]={0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,1 ,0 ,2 ,1 ,2 ,2 ,2 ,2 ,1 ,2 ,0 ,1 ,0 }; #define check (nextx>=0 && nextx<3 && nexty> =0 && nexty<3) int manhadun (string s) int sum=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<9 ;i++){ int t = s[i]-'0' ; if (t) sum += abs (i/3 -goer[t][0 ])+abs (i%3 -goer[t][1 ]); } return sum; } int astar (string s) unordered_map <string,int > um; priority_queue <pair<int ,string>> q; q.push ({-manhadun (s),s});um[s]=0 ; while (!q.empty ()){ auto a=q.top ();q.pop (); string st = a.second; if (st==goal) return um[st]; int Index = st.find ('0' ); int x=Index/3 ,y=Index%3 ; for (int i=0 ;i<4 ;i++){ nextx=x+explore[i][0 ];nexty=y+explore[i][1 ]; if (check){ string t=st; swap (t[Index],t[nextx*3 +nexty]); if (!um.count (t)){ um[t]=um[st]+1 ; q.push ({-(um[t]+manhadun (t)),t}); } } } } } int main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); cin >> start; cout << astar (start) << '\n' ; return 0 ; }
回溯与剪枝
当递归所衍生出的子节点不符合条件 时,就该“看到不对劲就撤退”——中途停止并返回 。这个思路就是回溯 。在回溯中用于减少子节点 的拓展函数就是剪枝函数 。
其难度主要在于拓展子节点的时候如何构造停止递归并返回的条件。
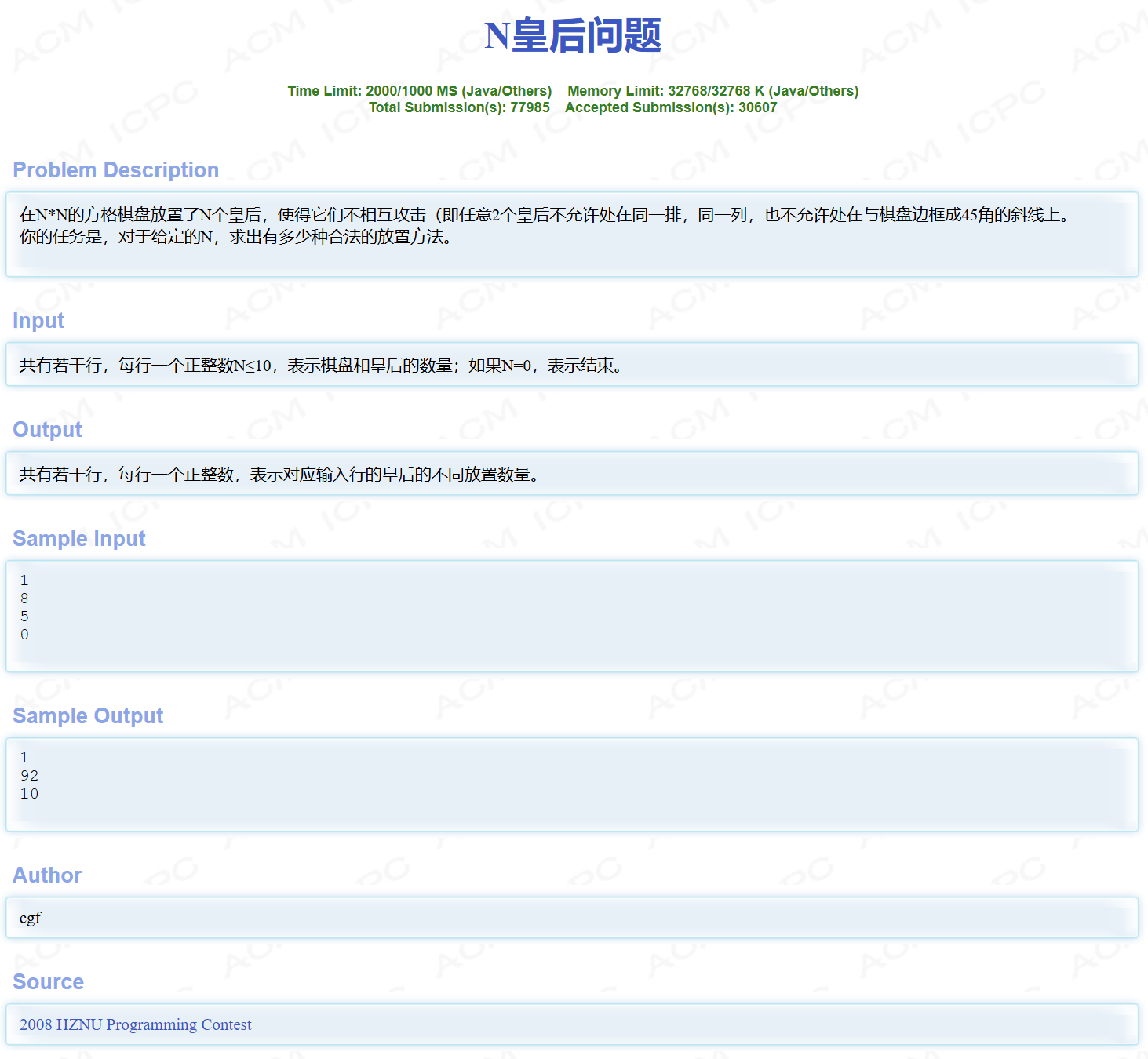
以HDU 2553 N皇后为例
题目
不同行: old_x != new_x
不同列: old_y != new_y
不同对角线: abs(old_x - new_x) != abs(old_y - new_y)
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int n,lie[11 ],ans[11 ],sum;bool check (int newx,int newy) for (int i=0 ;i<newx;i++) if (lie[i]==newy || abs (i-newx)==abs (lie[i]-newy)) return false ; return true ; } void dfs (int newx) if (newx==n){ sum++; return ; } for (int newy=0 ;newy<n;newy++){ if (check (newx,newy)){ lie[newx]=newy; dfs (newx+1 ); } } } int main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); for (n=0 ;n<=10 ;n++){ memset (lie,0 ,11 ); sum=0 ; dfs (0 ); ans[n]=sum; } while (cin >> n){ if (n==0 ) return 0 ; cout << ans[n] << '\n' ; } return 0 ; }
欧几里得算法(辗转相除法) 求最大公约数
原理是:两个整数的最大公约数等于其中较小的那个数和两数相除余数的最大公约数
gcd(a,b)=gcd(b,a%b)
用递归来实现
1 2 3 int gcd (int a,int b) return b==0 ? a : gcd (b,a%b); }
素数筛
试除法
设$ n=a \times b , 有 ,有 , 有 ,令 ,令 ,令 , 只要检查 ,只要检查 , 只要检查 内的数,如果 内的数,如果 内的数,如果 不是素数,就能找到一个 不是素数,就能找到一个 不是素数,就能找到一个 。试除法的复杂度是 。试除法的复杂度是 。试除法的复杂度是 ,对于 ,对于 ,对于
1 2 3 4 5 6 bool is_prime (int n) if (n<=1 ) return false ; for (int i=2 ;i*i<=n;i++) if (n%i==0 ) return false ; return true ; }
埃拉托斯特尼筛法(埃氏筛) 从2开始,不断筛掉2的倍数,3的倍数,5的倍数,7的倍数,11的倍数…
埃氏筛简单易用,其时间复杂度为$ O\left(n \log \log _2 n)\right. , 近似于 ,近似于 , 近似于
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const int MAXN = 1e7 +5 ; vector <int > prime; bool Visit[MAXN]; void sushu (int n) for (int i=2 ;i*i<=n;i++){ if (!Visit[i]) for (int j=i*i;j<=n;j+=i) Visit[j]=true ; } for (int i=2 ;i<=n;i++) if (!Visit[i]) prime.push_back (i); }
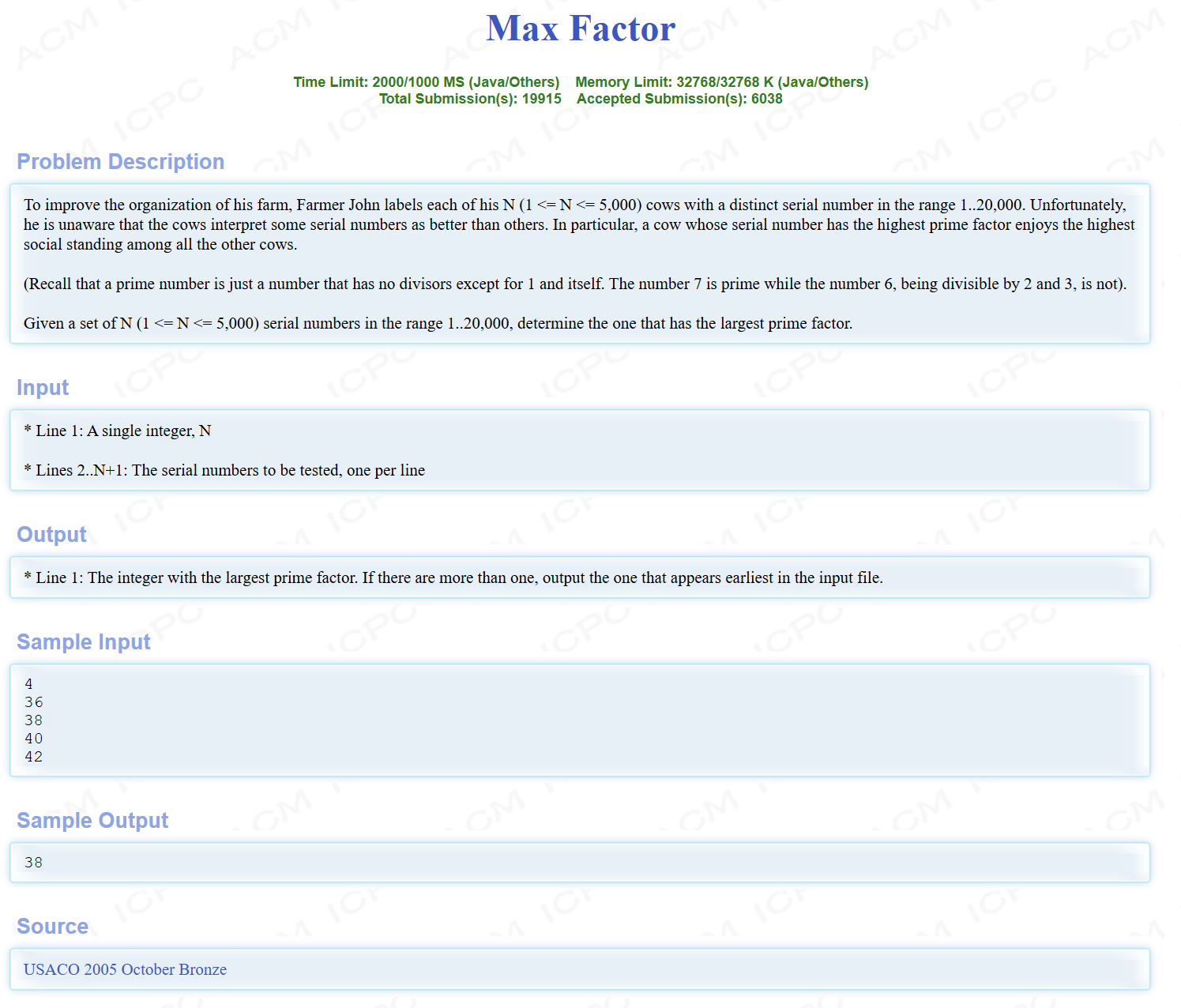
以HDU 2710为例
题目
在一组数中找到有最大质因数的那个,就用埃氏筛来找质数。
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int maxn = 1e5 ;bool Visit[maxn+5 ];vector <int > prime; void sushu () for (int i=2 ;i*i<=maxn;i++) if (!Visit[i]) for (int j=i*i;j<=maxn;j+=i) Visit[j]=true ; for (int i=2 ;i<=maxn;i++) if (!Visit[i]) prime.push_back (i); } int suyin (int n) if (n==1 ) return 1 ; for (int i=2 ;i*i<=n;i++){ if (!(n%i) && !Visit[n/i] && !Visit[i]) return n/i; } return 0 ; } int main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); sushu (); int n,cache; pair<int ,int >mx={0 ,0 }; cin >> n; while (n--){ cin >> cache; int t=suyin (cache); if (t!=mx.first) mx=max (mx,{suyin (cache),cache}); } cout << mx.second; return 0 ; }
鸽巢原理
鸽巢原理,即抽屉原理,其主要内容是: 把 n+1 个物体放进 n 个盒子,至少有一个盒子包含两个或更多物体.
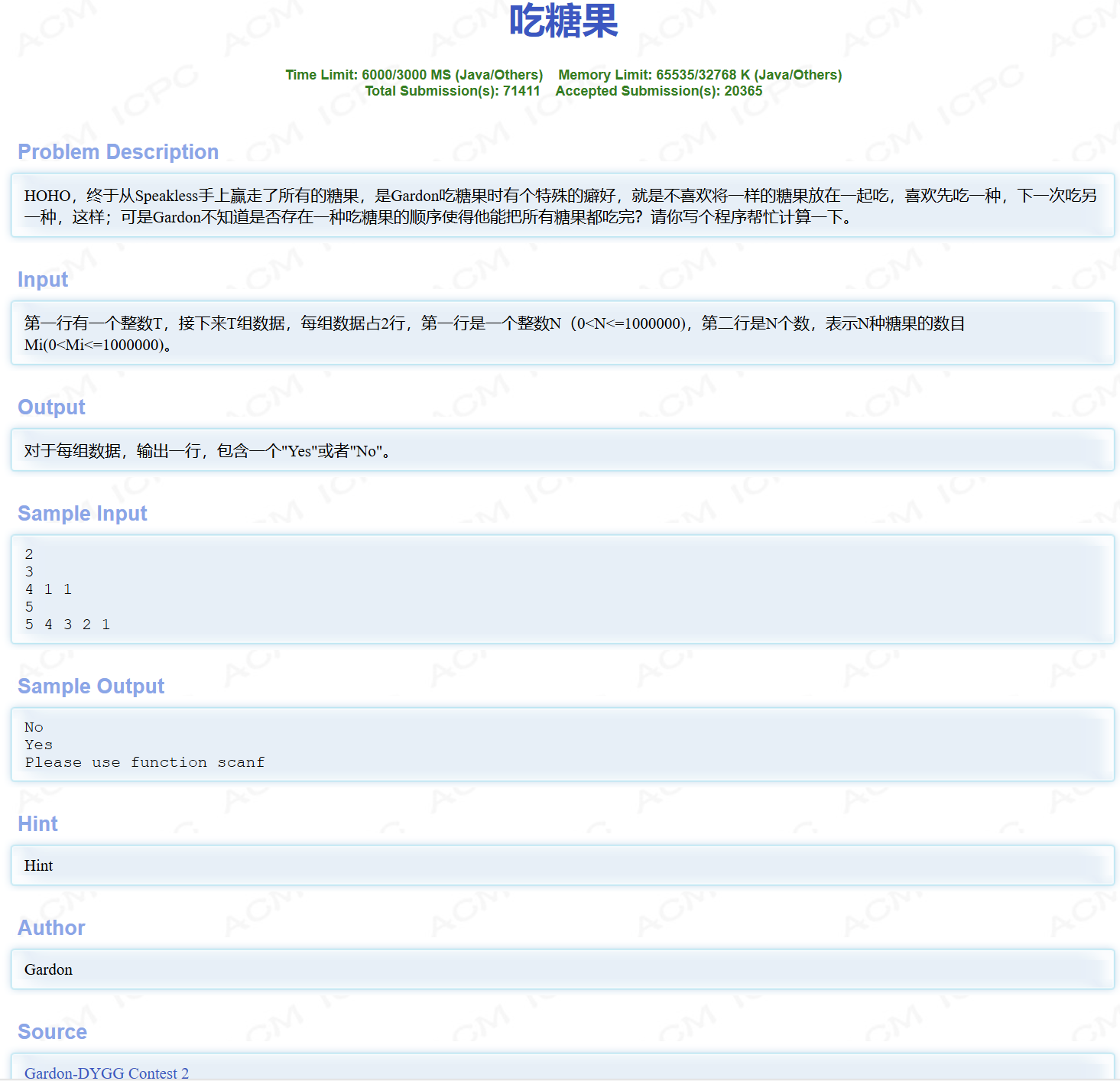
题目
以HDU 1205举例
这题如果去模拟的话还是比较麻烦,但是如果用鸽巢原理就很简单.
隔板法: 找出最多数量的那种糖果, 把它看成n个隔板,每个隔板的右边放置其他糖果.
令其他糖果总数为s,
如果 s<n-1 ,一定无解,这会使两个隔板之间没有其他糖果
如果 s>= n-1,一定有解,因为隔板的数量比剩下每种糖果的数量都多,因此不会有相邻同种糖果.
(看似简单的一题通过率仅28.5% , 这题有坑! 可能出现1e6 * 1e6的情况 , 不得不#define int long long)
代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;#define int long long signed main (void ) ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); int t,n; cin >> t; while (t--){ cin >> n; int mx=0 ,s=0 ,ai; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ cin >> ai; mx=max (mx,ai); s+=ai; } s-=mx; cout << ((s<mx-1 )?"No\n" :"Yes\n" ); } return 0 ; }